Gold rises on Middle East crisis, US core PCE inflation remains in spotlight
- Gold price rebounds sharply even though Fed policymakers maintain a hawkish narrative.
- The US Dollar remains firm as market expectations for early Fed rate cuts ease.
- Investors await the US core PCE inflation data for fresh guidance.
Gold price (XAU/USD) discovers strong buying interest in Wednesday’s early New York session despite Federal Reserve (Fed) policymakers are not interested in lowering interest rates anytime in the first half of 2024. Higher interest rates are negative for non-yielding Gold as they increase the opportunity cost of holding the precious metal.
For fresh cues about the timing for rate cuts, investors will focus on the United States core Personal Consumption Expenditure price index (PCE) data for January, which will be published on Thursday. Market expectations for rate cuts will be trimmed if the underlying inflation data turns out stickier than expectations. Such an outcome could trigger a downside move in Gold price.
On the geopolitical front, tensions between Israel and Hamas intensified as both nations have downplayed expectations of a ceasefire. Meanwhile, Palestine-backed Hamas said that it fired a number of rockets toward northern Israel.
Downbeat US Durable Goods Orders data for January released on Tuesday failed to catalyze gains in Gold price. Fresh orders for Durable Goods were down by 6.1%, while investors projected a decline of 4.5%. Weak demand for durable goods indicates a poor outlook for consumer spending.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price bounces back while US Dollar remains firm
- Gold price rebounds above $2,030 as geopolitical tensions escalate.
- Investors focus majorly on the United States core PCE price index data for January, which will be published on Thursday.
- The underlying inflation data will provide cues about when the Federal Reserve could consider a dovish shift in its monetary policy stance.
- Expectations are for the core PCE price index to have grown by 0.4% on a month-on-month basis in January against a 0.2% increase in December. Annually, the underlying inflation data is forecast to have decelerated to 2.8% from 2.9% in December.
- Sticky price pressures would allow Fed policymakers to argue in favor of keeping interest rates restrictive in the first half of 2024.
- Most Fed policymakers want to see more evidence to confirm that inflation will return sustainably to the 2% target before cutting rates.
- Currently, market expectations for rate cuts are considerably aligned with Fed policymakers who see no need to rush to reduce interest rates.
- The CME FedWatch tool shows that interest rates will remain unchanged in the range of 5.25%-5.50% in the March and May policy meetings. For the June meeting, traders see a 50% chance for a rate cut by 25 basis points (bps).
- On Tuesday, Federal Reserve Governor Michelle Bowman also supported keeping interest rates steady as early rate cuts could stall progress in inflation easing towards 2% or resurge price pressures.
- Michelle Bowman added that strong inflation readings in January and a tight labor market suggest slowing progress in inflation declining to 2%.
- Meanwhile, the US Dollar rally has paused for a while as the second estimate of Q4 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) indicates that the economy grew by 3.2%, against expectations of 3.3%.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which gauges the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, soars above 104.00 as uncertainty over US economic data has improved the appeal for safe-haven assets.
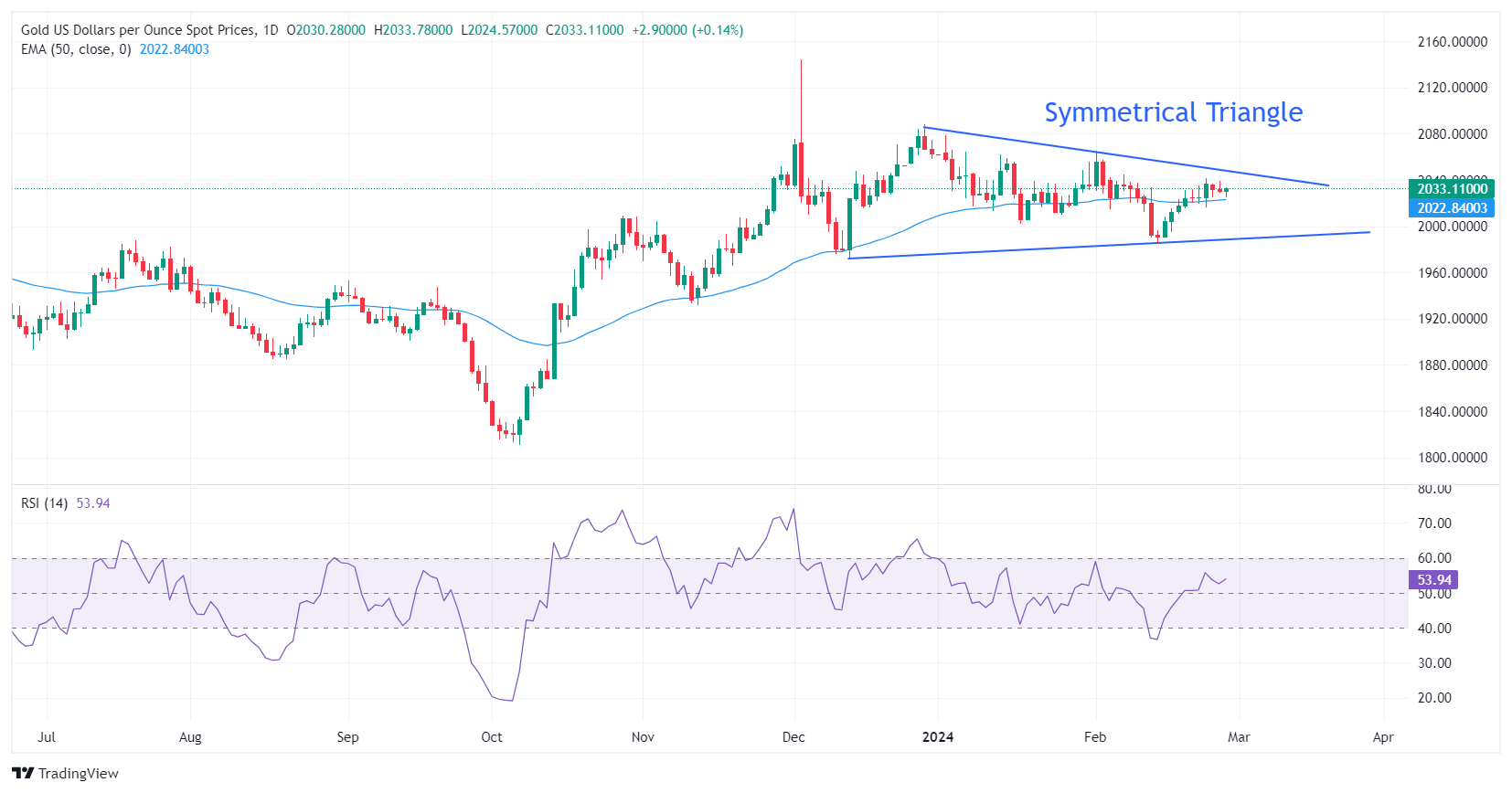
Technical Analysis: Gold price aims to recapture $2,040
Gold price rises toward the downward-sloping border of the Symmetrical Triangle pattern, which is plotted from the December 28 high at $2,088. The upward-sloping border of the chart pattern is placed from the December 13 low at $1,973.
The triangle could break out in either direction. However, the odds marginally favor a move in the direction of the trend before the formation of the triangle – in this case, up. A decisive break above or below the triangle boundary lines would indicate a breakout is underway.
The 14-period Relative Strength Index (RSI) oscillates in the 40.00-60.00 region, which indicates indecisiveness among investors.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates.
When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money.
When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions.
The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system.
It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
