Canadian Dollar backslides on Monday after manufacturing PMIs broadly miss the mark
- Markets kick off NFP week pricing in a first Fed rate cut in November.
- Canada reveals unexpected downturn in Manufacturing PMI data.
- CAD traders will be gearing up for a midweek BoC rate call as NFP Friday looms.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) is broadly lower on Monday after May’s S&P Canadian Global Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) figures missed the mark. A similar miss in ISM US Manufacturing PMIs has left the Canadian Dollar and the US Dollar (USD) battling for second place.
Canada has spent 13 months with manufacturing PMI surveys printing below the key 50.0 level as industry leaders continue to grapple with a mouldering Canadian economy. CAD traders will also be looking ahead to Wednesday’s rate call from the Bank of Canada (BoC) as markets lean further into hopes of a rate trim from the Canadian central bank. According to a recent Reuters poll, 22 of 29 surveyed economists expect a 25-basis-point rate cut from the BoC on June 5.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar weakens, but Greenback weakens faster
- Canadian S&P Manufacturing PMI in May eased to 49.3 from 49.4, missing the forecasted increase to 50.2.
- Markets broadly ignored the S&P Global US PMI to focus on a miss in the US ISM Manufacturing PMI, which eased to 48.7 from 49.2 in May, down from the forecast increase to 49.6.
- Wednesday looms ahead with the BoC’s latest rate call, where markets are anticipating a quarter-point cut.
- Wednesday also brings ADP Employment Change for May, a common (albeit volatile) preview of Friday’s US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) jobs report.
- Canadian labor figures due Friday will be overshadowed by market reactions to US NFP.
Canadian Dollar PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Canadian Dollar (CAD) against listed major currencies today. Canadian Dollar was the weakest against the New Zealand Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.48% | -0.48% | -0.67% | 0.00% | -0.50% | -0.86% | -0.83% | |
| EUR | 0.48% | 0.03% | -0.19% | 0.49% | -0.14% | -0.38% | -0.37% | |
| GBP | 0.48% | -0.03% | -0.14% | 0.46% | -0.11% | -0.47% | -0.40% | |
| JPY | 0.67% | 0.19% | 0.14% | 0.64% | 0.20% | -0.04% | -0.01% | |
| CAD | -0.01% | -0.49% | -0.46% | -0.64% | -0.54% | -0.87% | -0.86% | |
| AUD | 0.50% | 0.14% | 0.11% | -0.20% | 0.54% | -0.25% | -0.25% | |
| NZD | 0.86% | 0.38% | 0.47% | 0.04% | 0.87% | 0.25% | -0.02% | |
| CHF | 0.83% | 0.37% | 0.40% | 0.00% | 0.86% | 0.25% | 0.02% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Canadian Dollar from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent CAD (base)/USD (quote).
Technical analysis: Canadian Dollar stumbles on Monday despite USD/CAD pumping the brakes
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) is broadly lower on Monday, shedding weight across the board and struggling to hold ground against the US Dollar. The CAD is down around a full percent against the Japanese Yen (JPY) and the Swiss Franc (CHF). A softening Greenback will have to settle for second place on Monday as the declining US Dollar is struggling to catch up to the weakening CAD.
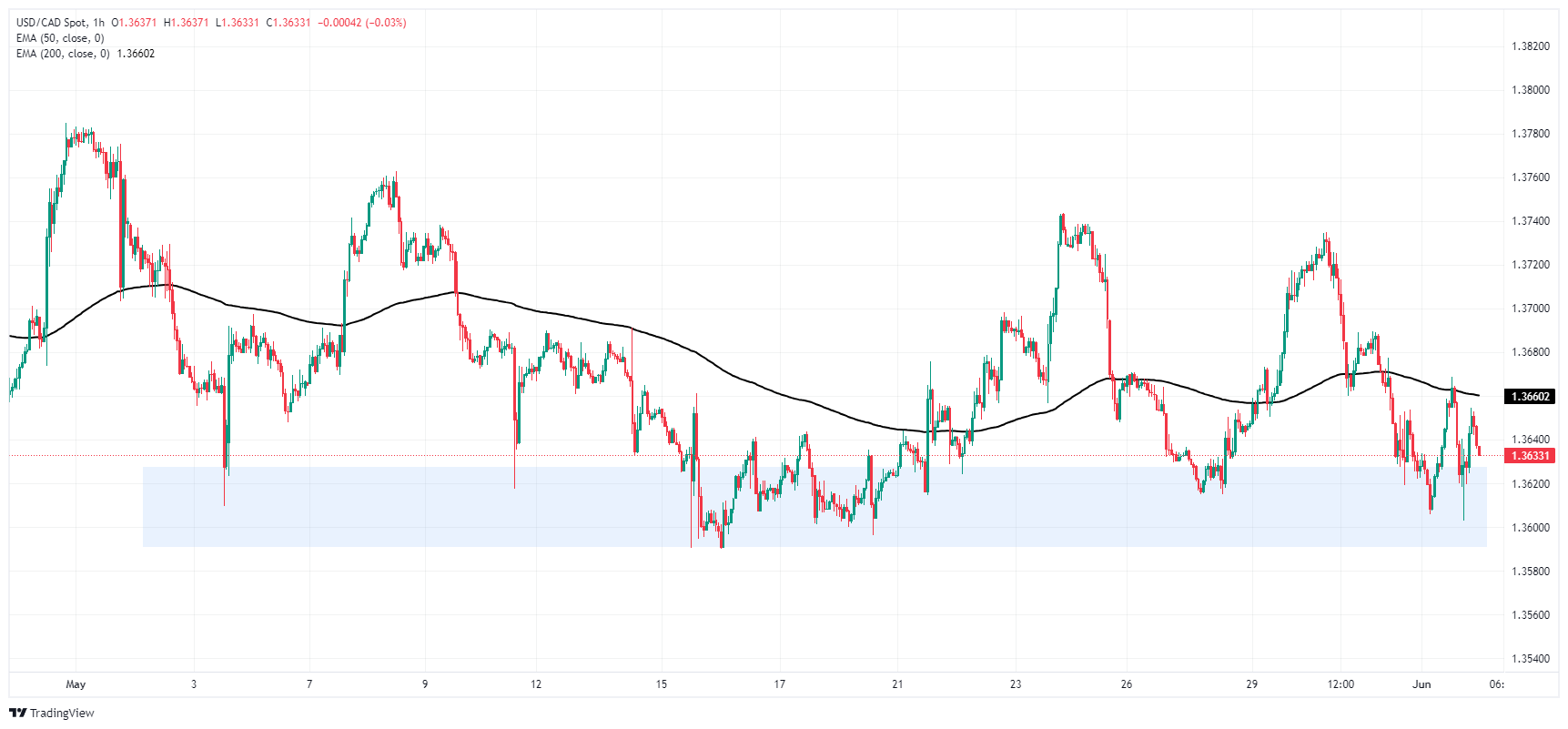
USD/CAD slumped once more into a familiar demand zone near the 1.3600 handle, but firmer bidding on the Greenback side keeps the pair in range of Monday’s early peak near 1.3660. The pair has been in a rough consolidation pattern since the beginning of May, but highs are drifting lower as CAD strength looks set to fade further.
A long-term technical floor is still priced in at the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.3560, and USD/CAD appears mired in congestion at the 50-day EMA near 1.3645. A move higher will see the pair grappling with 2024’s peak bids near 1.3850.
USD/CAD hourly chart
USD/CAD daily chart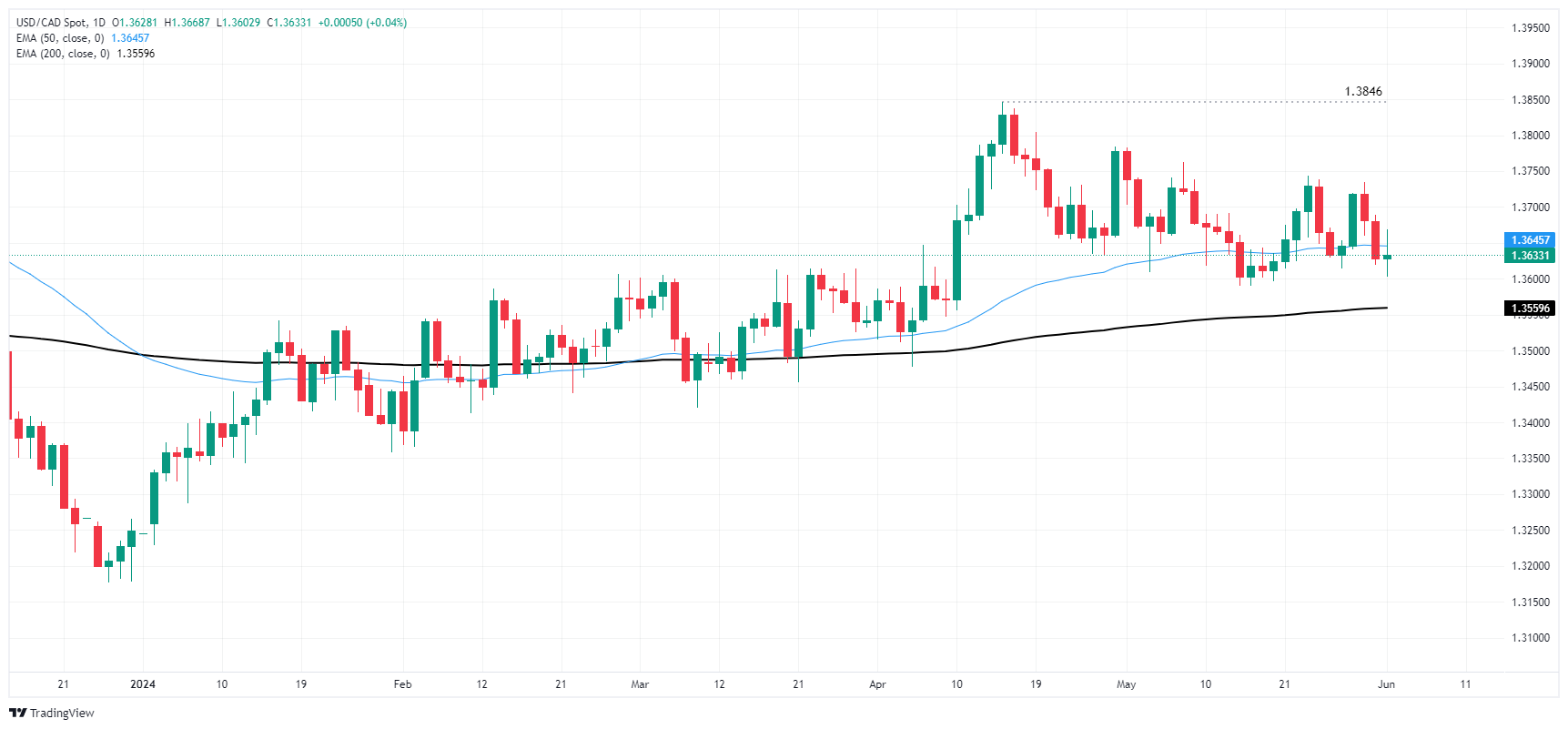
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.
