Canadian Dollar firms up against Greenback on Friday
- The Canadian Dollar was broadly softer, but gained against USD on Friday.
- Canada is due to release its latest CPI inflation update next week.
- US consumer sentiment ticked higher in August, sparking an uptick in risk appetite.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) was overall softer on Friday, shedding weight across the currency board, but still found gains against the risk-appetite-weakened Greenback to wrap up the trading week. Broad-market risk sentiment improved further on Friday as upbeat US data prints help to temper recent investor fears of a US recession.
Canada will be bringing its latest round of inflation data next Tuesday, and CAD traders will be looking for stable prints in Canadian Consumer Price Index (CPI) figures to keep sentiment on-balance.
Daily digest market movers: CAD soft on Friday, but Greenback softer
- Markets focused squarely on US consumer sentiment figures on Friday, finding one last reason to hit the short button on Greenback flows.
- The University of Michigan’s Consumer Sentiment Index rose to 67.8 in August, up from the previous 66.4.
- Market sentiment lurched higher after the sentiment index handily beat the forecast of 66.9.
- Consumer 5-year Inflation Expectations and held steady at 3.0% in August, unchanged from the previous month.
- The Jackson Hole Symposium begins next Thursday, plenty of central bank policymaker appearances are expected.
Canadian Dollar price forecast: Greenback slide gives CAD fresh leg into near-term highs
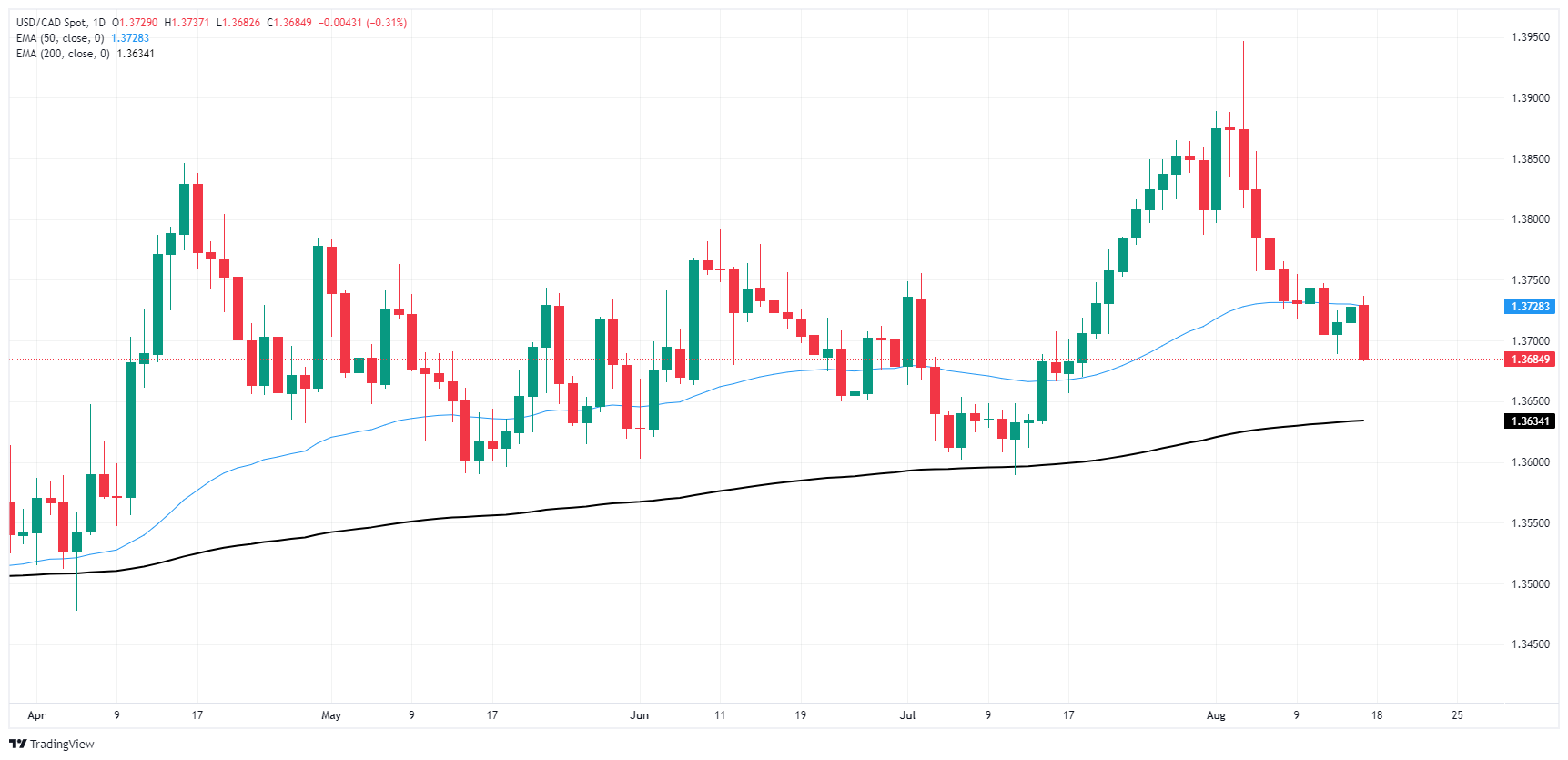
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) found room up top thanks to a weakening Greenback on Friday, climbing into a three-week high and sending USD/CAD below the 1.3700 handle.
The pair found a technical rejection from the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 1.3728, with price action hamstrung in the midrange between the 50-day EMA and the 200-day EMA at 1.3634.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.
