Gold remains capped under $2,500 as traders await fresh drivers
- Gold price trades in negative territory for the third consecutive day in Tuesday’s Asian session.
- The rising US Fed rate cut bets and geopolitical risks might help limit Gold’s losses.
- Investors await the US August ISM PMI for fresh impetus.
The Gold price (XAU/USD) loses ground amid the stronger US Dollar (USD) and higher US Treasury bond yields on Tuesday. Nonetheless, the anticipation that the US Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut interest rates in September might underpin the precious metal price as lower interest rates reduce the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding gold. Additionally, the ongoing geopolitical tensions in the Middle East might boost safe-haven assets like Gold.
Looking ahead, the Institute for Supply Management’s (ISM) Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) will be published on Tuesday. The highlight for this week will be the US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) for August, which might determine the pace of the interest rate cut by the Fed and could influence the Gold price in the near term.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price faces selling pressure amid the rebound of USD
- Protests broke out across Israel in fresh fury on Monday over the government’s failure to secure a ceasefire-for-hostages deal with Hamas, per CNN. The move is fuelled by the killing in Gaza of six hostages, whose bodies were retrieved by Israeli soldiers this weekend.
- China’s Caixin Manufacturing PMI climbed to 50.4 in August from 49.8 in July, above the market consensus of 50.0.
- The US ISM Manufacturing PMI for August is expected to improve to 47.5 in August from 46.8 in July, while the Services PMI is estimated to drop to 51.1 in August versus 51.4 prior.
- The US economy is expected to see 163K job additions in August. The Unemployment Rate is expected to tick lower to 4.2%.
- The markets are now pricing in a nearly 69% possibility of 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the Fed in September, while the chance of a 50 bps reduction is standing at 31%, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
Technical Analysis: Gold price maintains positive momentum in the longer term
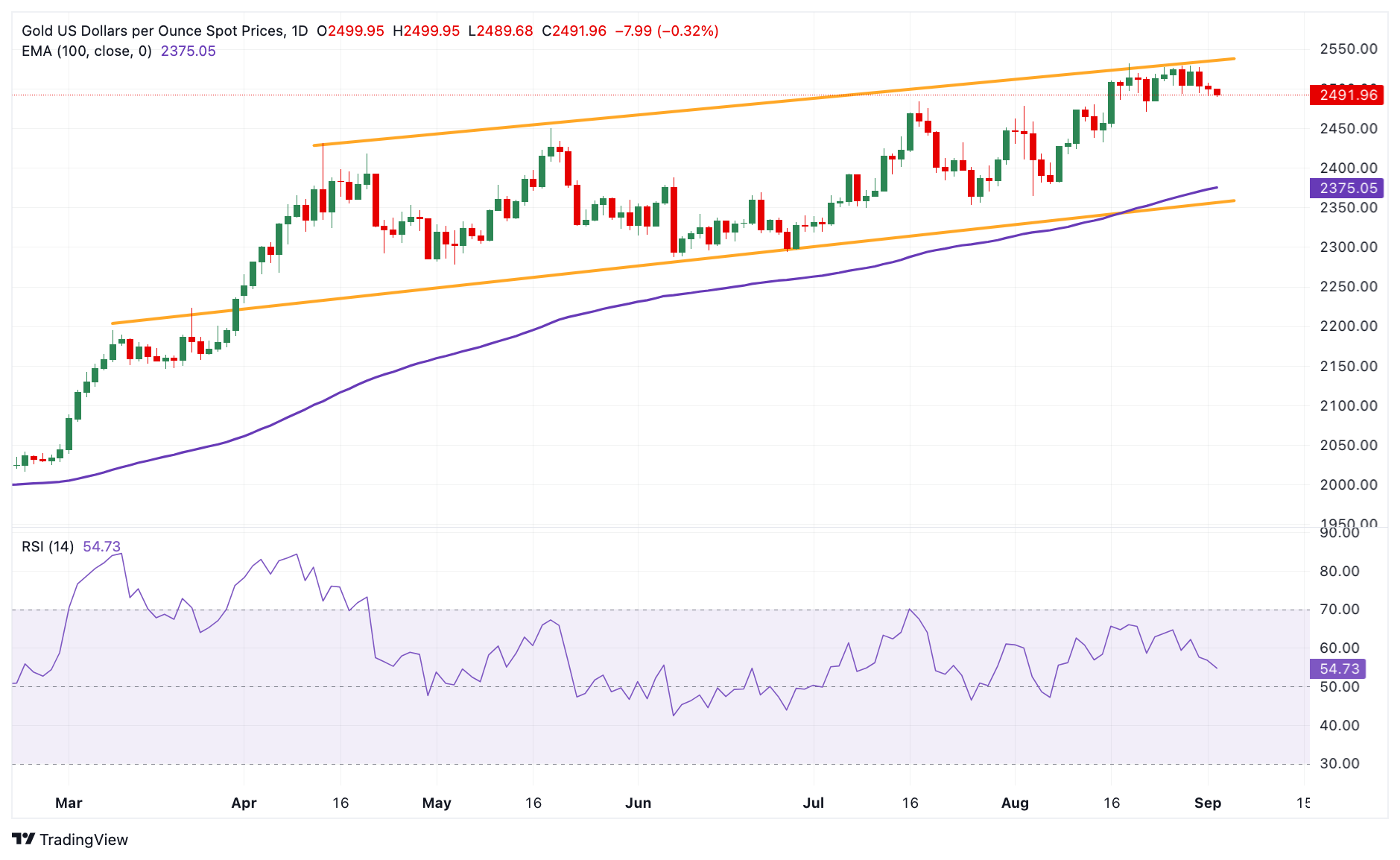
The Gold price drifts lower on the day. According to the daily chart, the constructive outlook of the precious metal prevails as the price is well above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The upward momentum is reinforced by the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI), which stands above the midline around 55.70, suggesting the climb is more likely to resume than to reverse.
The key resistance level for XAU/USD emerges in the $2,530-$2,540 zone, portraying the five-month-old ascending channel’s upper boundary and the all-time high. A decisive break above the mentioned level could see a rally to the $2,600 psychological level.
On the flip side, the low of August 22 at $2,470 acts as an initial support level for the yellow metal. A break below this level could drag the price further south to $2,432, the low of August 15. The next contention level to watch is $2,372, the 100-day EMA.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
