Mexican Peso strengthens on Sheinbaum’s first day at office
- Mexican Peso on the front foot following as Sheinbaum’s take office.
- Traders await President-Elect Claudia Sheinbaum’s inaugural remarks.
- Stronger than expected US JOLTS data and Powell’s comments support a bullish bias in USD/MXN.
The Mexican Peso appreciated sharply against the Greenback on Tuesday after President Claudia Sheinbaum took office and delivered her first speech in the Mexican Congress. The Peso recovered some ground as Sheinbaum reassured investors that their investments remained secure. At the time of writing, the USD/MXN dropped some 0.37% and traded at 19.60 amid heightened tensions in the Middle East.
Wall Street reflects a downbeat market mood due to heightened geopolitical risks. This sparked flows toward the Greenback due to its safe-haven status, which was detrimental to the Peso’s emerging market status.
Mexico’s economic docket remains absent, with traders awaiting remarks from President Claudia Sheinbaum as she takes office. Across the north of the border, the US schedule featured the release of the August JOLTS report, which was better than expected and exceeded the July number.
The Institute for Supply Management (ISM) revealed the September Manufacturing PMI, which remained in contractionary territory but was unchanged compared to August.
On Monday, Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell revealed that the central bank is in no rush to lower borrowing costs while foreseeing 50 basis points of easing toward the end of 2024.
Given the backdrop, the USD/MXN is expected to remain upwardly biased after Powell resisted expectations of aggressive easing by the Fed.
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso advances despite geopolitical risks
- Mexican political turmoil eases as market participants prepare for the change of president on October 1, a bank holiday in Mexico.
- According to the swaps markets, Banxico is expected to lower borrowing costs by 175 bps by the end of 2025.
- The US Department of Labor revealed that the August Job Openings & Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) increased from 7.711 million to 8.04 million, exceeding estimates of 7.655 million.
- The ISM Manufacturing PMI in September rose by 47.2, unchanged from the previous reading, but it missed estimates of 47.5.
- Last week Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic commented that he will closely monitor jobs data to assess the Fed’s policy stance. He indicated that he is open to cutting rates by 50 basis points (bps) while acknowledging that he is not yet ready to declare victory on inflation.
- Market participants have put the odds of a 25 bps cut at 61.6%. According to the CME FedWatch Tool, the chances for a larger 50 bps cut diminished to 38.4%.
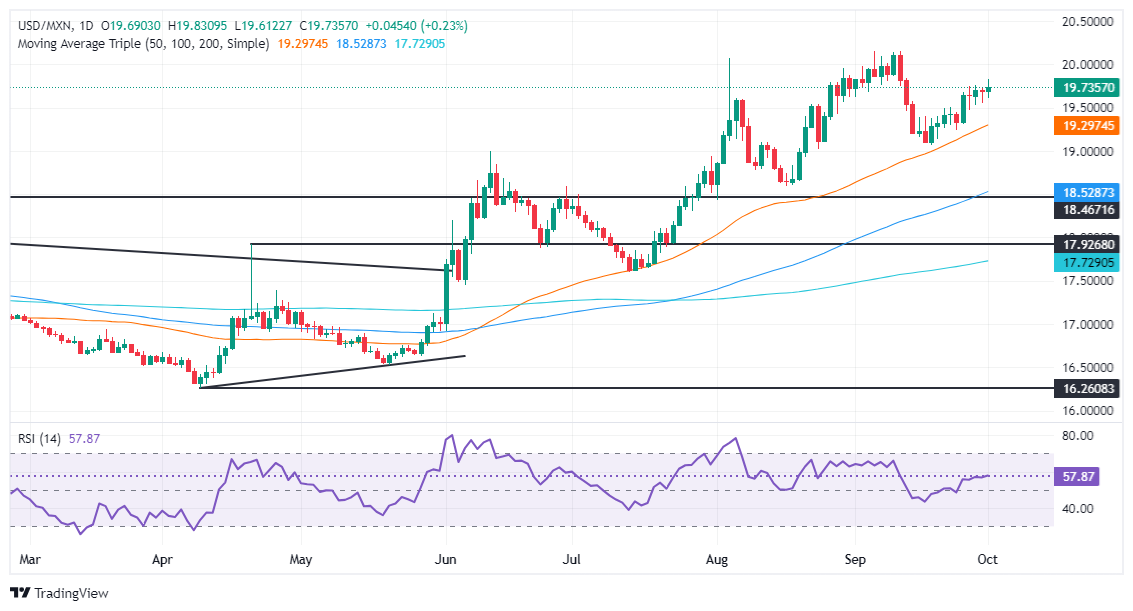
USD/MXN technical analysis: Mexican Peso gains as USD/MXN drops toward 19.60
The USD/MXN uptrend remains intact and resumed for the fifth consecutive day, with buyers gaining momentum. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) shows that bulls are in charge. This means that the exotic pair could test higher prices in the near term.
If USD/MXN clears the psychological 20.00 figure, the next resistance would be the YTD peak of 20.22. Further strength will expose the September 28, 2022, high of 20.57, followed by the 21.00 mark.
Conversely, If USD/MXN drops below 19.50, the next support would be the September 24 swing low of 19.23 before the pair moves toward the September 18 low of 19.06. Once those levels are surpassed, the 19.00 figure emerges as the following line of defense.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.
