Aussie Dollar slips on robust US data, eyes on next week’s US inflation
- AUD/USD falls following robust US Nonfarm Payrolls data, reducing the likelihood of aggressive Fed rate cuts.
- Fed Chair Powell signals slower pace of easing, with markets now pricing in a 25 bps cut for November.
- Australian data shows mixed results with strong Retail Sales and trade surplus but ongoing manufacturing contraction and slowing business activity.
The Australian Dollar dropped during the North American session after September’s jobs report in the United States (US), suggesting that the Federal Reserve (Fed) would not cut rates by 50 basis points (bps) at the November meeting. The AUD/USD trades at 0.6796, down over 0.60%.
The AUD/USD extended its losses following September’s monster Nonfarm Payrolls report in the US, which lowered the Unemployment Rate. Average Hourly Earnings were mixed, though overall the data relieved the Fed from lowering rates aggressively.
In September, the Fed cut rates by 50 bps. The swaps markets showed that investors had earlier been eyeing another one of the same size in the November or December meeting. However, Fed Chair Jerome Powell pushed against this stance on Monday, saying that officials foresaw 50 bps of easing in total at the end of 2024 and that the US central bank is in no rush to cut rates.
According to CME FedWatch Tool data, the markets had priced in a 25 bps cut at the November meeting regarding Fed interest rate probabilities.
Aside from this, Australia’s data witnessed a solid Retail Sales report, and the Balance of Trade in August printed a surplus. Although those conditions could prevent the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) from cutting rates, business activity in the manufacturing sector, via the Judo Bank Manufacturing PMI, contracted for eight straight months.
On the other hand, the Judo Bank Services PMI slowed sharply, while Building Permits plummeted, hinting at an ongoing economic slowdown.
Next week, Australia’s economic docket will feature Business and Consumer Confidence data, RBA speakers, and the RBA’s latest meeting minutes. On the US front, the schedule will feature the release of inflation data, jobless claims, and University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment.
Daily digest market movers: Australian Dollar depreciates on US data, geopolitical risks
- The Australian Dollar will likely remain pressured due to several factors. Geopolitical risks, such as over-the-weekend developments in the Middle East, could hurt risk appetite for the AUD.
- The Aussie’s economic docket will feature the NAB Business Confidence and the Westpac Consumer Confidence for September and October, respectively. Following that, traders eye RBA’s Hauser, Kent and Hunter speeches.
- US Nonfarm Payrolls increased by 254K in September, significantly surpassing the estimated 140K and the upwardly revised August figure of 159K. The Unemployment Rate fell from 4.2% to 4.1%, lower than expected.
- Average Hourly Earnings in September rose by 0.4% MoM, down from 0.5% in the previous month but exceeding forecasts of 0.3%.
- On a YoY basis, earnings per hour increased by 4% in the 12 months to September, surpassing estimates and improving on August’s figures of 3.8% and 3.9%.
- Market participants have ruled out a 50 bps cut from the Fed. The odds of a 25 bps cut stand at 95%, with only a 5% chance of rates being held unchanged, according to the CME FedWatch Tool data.
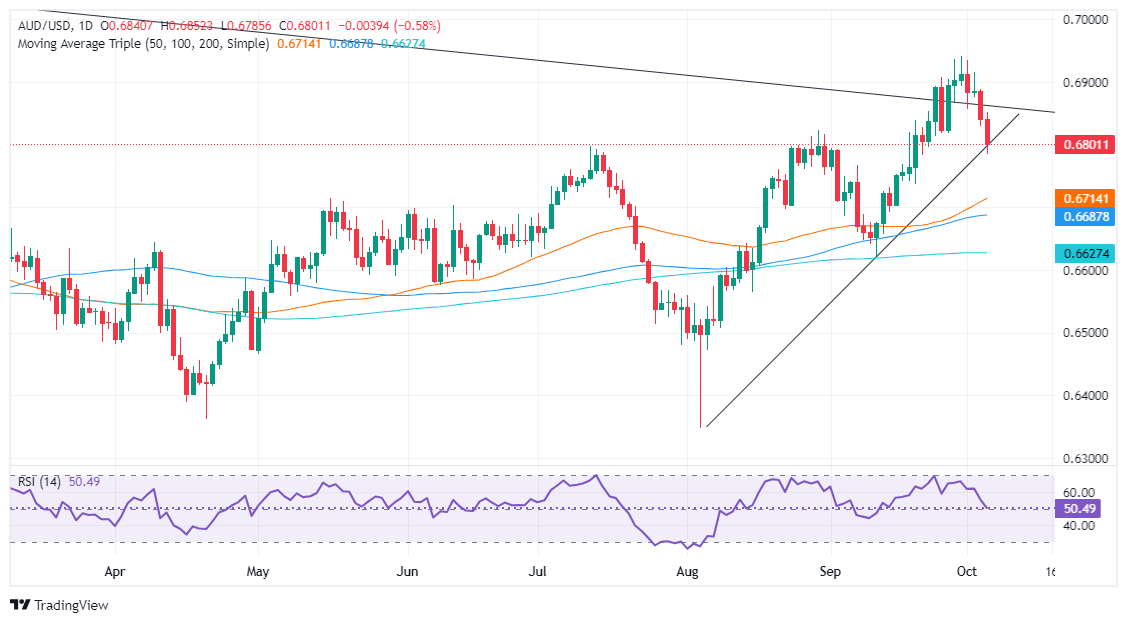
Technical analysis: Australian Dollar extends its losses below 0.6800
Despite retreacing below the 0.6800 figure, the AUD/USD remains upwardly biased. Momentum is mixed with the Relative Strength Index (RSI) remaining bullish but hinting at dropping into bearish territory.
The AUD/USD could accelerate its losses if it clears the September 6 peak at 0.6767. Once surrendered, the next demand area will be the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 0.6712.
On the other hand, if buyers lift the AUD/USD above 0.6800, the first supply zone will be the October 1, 2024 low of 0.6856. A breach of the latter will expose 0.6900 before retesting the year-to-date high of 0.6934.
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for Australia. Decisions are made by a board of governors at 11 meetings a year and ad hoc emergency meetings as required. The RBA’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means an inflation rate of 2-3%, but also “..to contribute to the stability of the currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and welfare of the Australian people.” Its main tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will strengthen the Australian Dollar (AUD) and vice versa. Other RBA tools include quantitative easing and tightening.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for currencies since it lowers the value of money in general, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Moderately higher inflation now tends to lead central banks to put up their interest rates, which in turn has the effect of attracting more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in the case of Australia is the Aussie Dollar.
Macroeconomic data gauges the health of an economy and can have an impact on the value of its currency. Investors prefer to invest their capital in economies that are safe and growing rather than precarious and shrinking. Greater capital inflows increase the aggregate demand and value of the domestic currency. Classic indicators, such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can influence AUD. A strong economy may encourage the Reserve Bank of Australia to put up interest rates, also supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a tool used in extreme situations when lowering interest rates is not enough to restore the flow of credit in the economy. QE is the process by which the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) prints Australian Dollars (AUD) for the purpose of buying assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from financial institutions, thereby providing them with much-needed liquidity. QE usually results in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops buying more assets, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It would be positive (or bullish) for the Australian Dollar.
