Australian Dollar extends its recovery ahead of US PPI data
- The Australian Dollar trades in positive territory for the second consecutive day in Friday’s Asian session.
- Reduced bets of deeper Fed rate cuts support the USD and weigh on the pair.
- Investors brace for the US PPI data, which is due on Friday.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) gains ground on Friday. Nonetheless, the lower odds of aggressive interest rate cuts from the US Federal Reserve (Fed) after the hotter-than-expected inflation data might lift the US Dollar (USD) and cap the upside for the pair.
In the absence of top-tier economic data releases from the Australia on Friday, the USD price dynamic will be the main driver for the AUD/USD. Investors will monitor the release of US Producer Price Index (PPI), which is due on Friday. The headline PPI is expected to show an increase of 1.6% YoY in September, while the core PPI is estimated to see a rise of 2.7% YoY during the same period. If the reports shows softer than expected outcome, this could weigh on the USD and acts as a tailwind for AUD/USD. Additionally, the preliminary of the Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index will be released later in the day.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar extends its recovery ahead of another US inflation data
- RBA Minutes from the September meeting showed board members overlooked the warning that there would be no rate cuts in the near future. The Australian central bank wants to keep its options open, watching whether the economy starts to pick up in the second half of the year.
- The US Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 2.4% YoY in September, compared to 2.5% in August, above the consensus of 2.3%, the US Department of Labor Statistics showed Thursday. The core CPI, excluding food and energy, climbed 3.3% YoY in September, above forecast and the previous reading of 3.2%.
- The US Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending October 4 rose to 258K, up from the previous week’s 225K. The figure was above the initial consensus of 230K.
- New York Fed President John Williams said on Thursday that he expects more rate cuts lie ahead as inflation pressures continue to moderate and the economy remains solid.
- Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee noted he sees a series of rate reductions over the next year to year and a half, noting that inflation is now near the Fed’s 2% target and the economy is about at full employment.
- Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic is open to the idea of skipping a rate cut in November if economic data still hasn’t aligned with the Fed’s target figures in time.
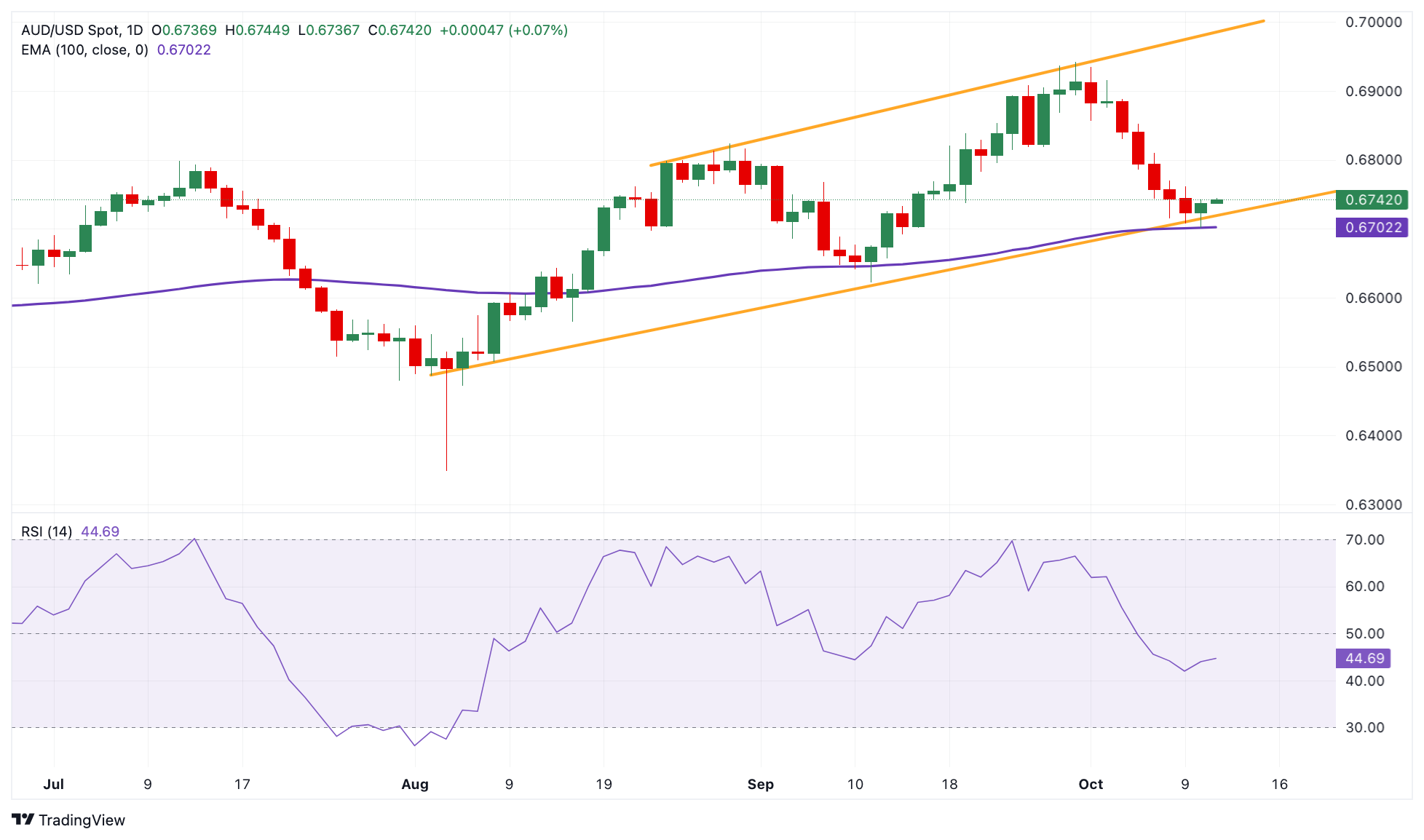
Technical Analysis: Australian Dollar maintains a positive view in the longer term
The Australian Dollar trades stronger on the day. According to the daily chart, the
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for Australia. Decisions are made by a board of governors at 11 meetings a year and ad hoc emergency meetings as required. The RBA’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means an inflation rate of 2-3%, but also “..to contribute to the stability of the currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and welfare of the Australian people.” Its main tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will strengthen the Australian Dollar (AUD) and vice versa. Other RBA tools include quantitative easing and tightening.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for currencies since it lowers the value of money in general, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Moderately higher inflation now tends to lead central banks to put up their interest rates, which in turn has the effect of attracting more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in the case of Australia is the Aussie Dollar.
Macroeconomic data gauges the health of an economy and can have an impact on the value of its currency. Investors prefer to invest their capital in economies that are safe and growing rather than precarious and shrinking. Greater capital inflows increase the aggregate demand and value of the domestic currency. Classic indicators, such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can influence AUD. A strong economy may encourage the Reserve Bank of Australia to put up interest rates, also supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a tool used in extreme situations when lowering interest rates is not enough to restore the flow of credit in the economy. QE is the process by which the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) prints Australian Dollars (AUD) for the purpose of buying assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from financial institutions, thereby providing them with much-needed liquidity. QE usually results in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops buying more assets, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It would be positive (or bullish) for the Australian Dollar.
