USD/INR drifts higher ahead of US Retail Sales data
- The Indian Rupee softens in Thursday’s Asian session.
- The continued selling of domestic equities by foreign portfolio investors weighs on the INR.
- The US September Retail Sales will be the highlight on Thursday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) trades with mild losses on the stronger US Dollar (USD) on Thursday. The significant outflows from Indian equities and USD demand from foreign banks and importers exert some selling pressure on the local currency.
However, the decline in crude oil prices amid easing fears over supply disruption in the Middle East might support the INR as India is the world’s third-largest oil consumer. Additionally, the routine foreign exchange interventions by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) could cap the downside for the Indian Rupee.
Traders will keep an eye on the US Retail Sales data for September, which is due later on Thursday. Also, the US weekly Initial Jobless Claims, Industrial Production and Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Survey will be released.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee remains weak amid foreign fund outflows
- India’s trade deficit stood at $20.78 billion in September from $29.65 billion in August, according to data released by the commerce ministry on Wednesday.
- India’s Exports rose marginally to 34.58 billion in September from 34.41 in the year-ago period. Meanwhile, Imports declined to 55.36 billion in September versus 64.36 billion prior.
- Foreign funds withdrew more than $7 billion from Indian equities in the month through October 14, the largest in over four years, according to Bloomberg.
- The US Retail Sales is estimated to rise to 0.3% in September from 0.1% in the previous reading.
- According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders have priced in a nearly 94% chance of a 25 basis points (bps) Fed rate cut in November.
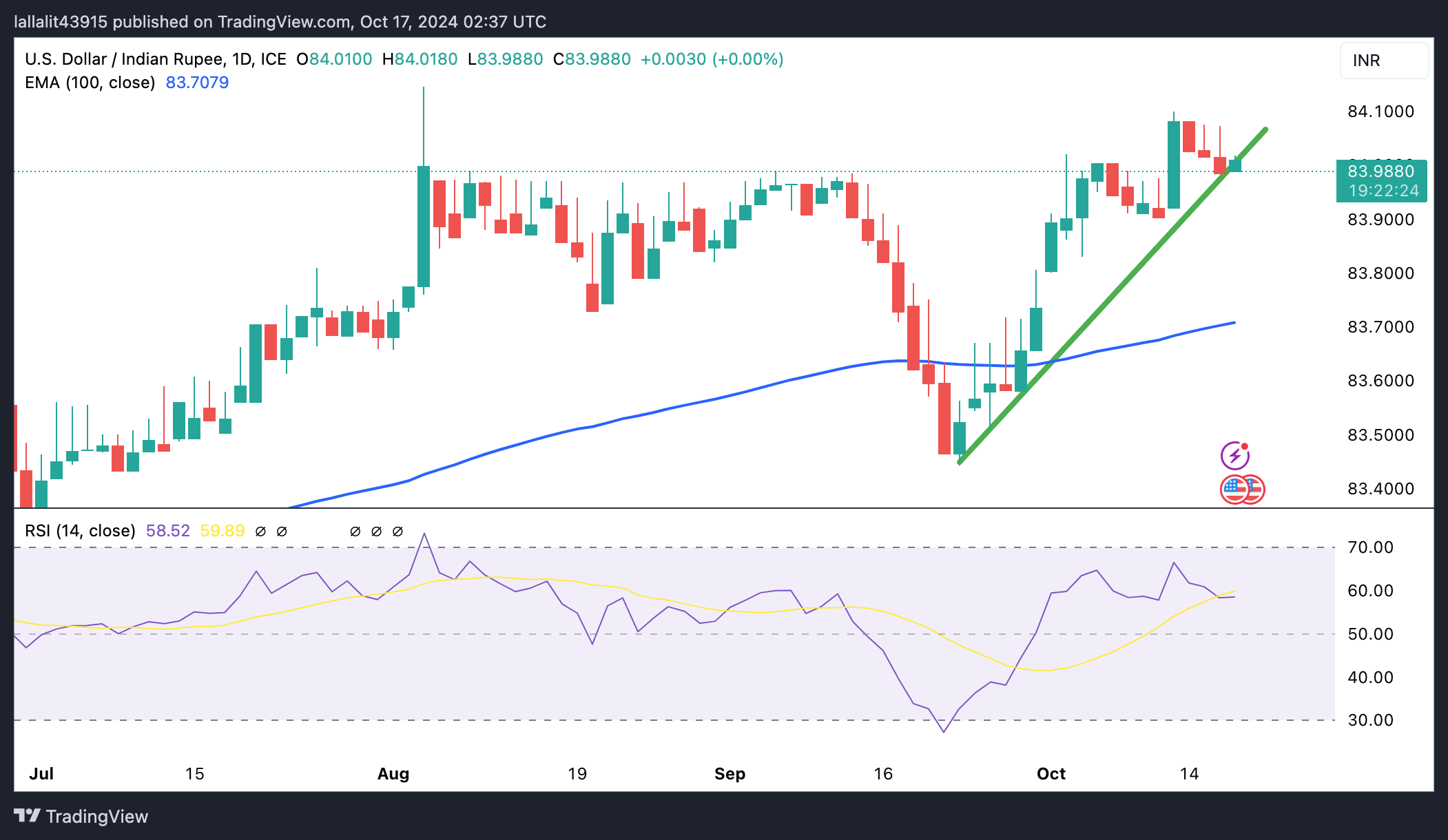
Technical Analysis: USD/INR’s constructive outlook remains intact
The Indian Rupee trades in negative territory on the day. Technically, the USD/INR pair keeps the bullish vibe as the price holds above the ascending trend line and the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. The upward momentum is supported by the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI), which is located above the midline near 58.80, hinting that the uptrend is more likely to gain traction than reverse.
Sustained trading above the all-time high of 84.15 could expose the pair to a possible move up to 84.50. Further north, the next upside barrier to watch is the 85.00 psychological level.
Bearish candlesticks below the rising trend line could lead to 83.90, the low of October 10. A breach of the mentioned level could pave the way to 83.70, the 100-day EMA. The next contention level is seen at 83.00, representing the round mark and the low of May 24.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
