USD/INR trades flat despite the firmer US Dollar
- The Indian Rupee holds steady in Monday’s early European session.
- Lower crude oil prices underpin the INR, but persistent Indian foreign outflows could cap its upside.
- Investors await the advanced US GDP growth numbers for Q3 on Wednesday ahead of NFP data.
The Indian Rupee (INR) trades on a flat note on Monday despite the stronger US Dollar (USD). The fall in crude oil prices could provide some support to the local currency as India is the world’s third-largest oil consumer. However, the upside of the INR might be limited amid sustained foreign outflows from domestic stocks and the expectation of a slower pace of the US Federal Reserve (Fed) rate cuts.
Investors will keep an eye on the advanced US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Annualized for the third quarter (Q3), which is due on Wednesday. The Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index for September will be released on Thursday. On Friday, the highly anticipated US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) will be in the spotlight.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Indian Rupee flat lines, the potential upside seems limited
- India’s economic growth is estimated to reach between 7.0% and 7.2% in the fiscal year 2024-25, according to Deloitte India’s latest Economic Outlook.
- The preliminary estimates showed that India’s HSBC Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) rose to 57.4 in October versus 56.5 prior. The Services PMI increased to 57.9 in October from a one-year low of 57.7 in September.
- The US Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index rose to 70.5 in October from 68.9 in the previous reading, beating expectations.
- The Durable Goods Orders declined by 0.8% MoM in September, above the market consensus of a 1% decline. Durable Goods Orders excluding transportation increased 0.4% in September.
- US rate futures have priced in a 97.7% possibility that the Fed will cut rates by 25 basis points (bps) in November, according to the CME FedWatch tool.
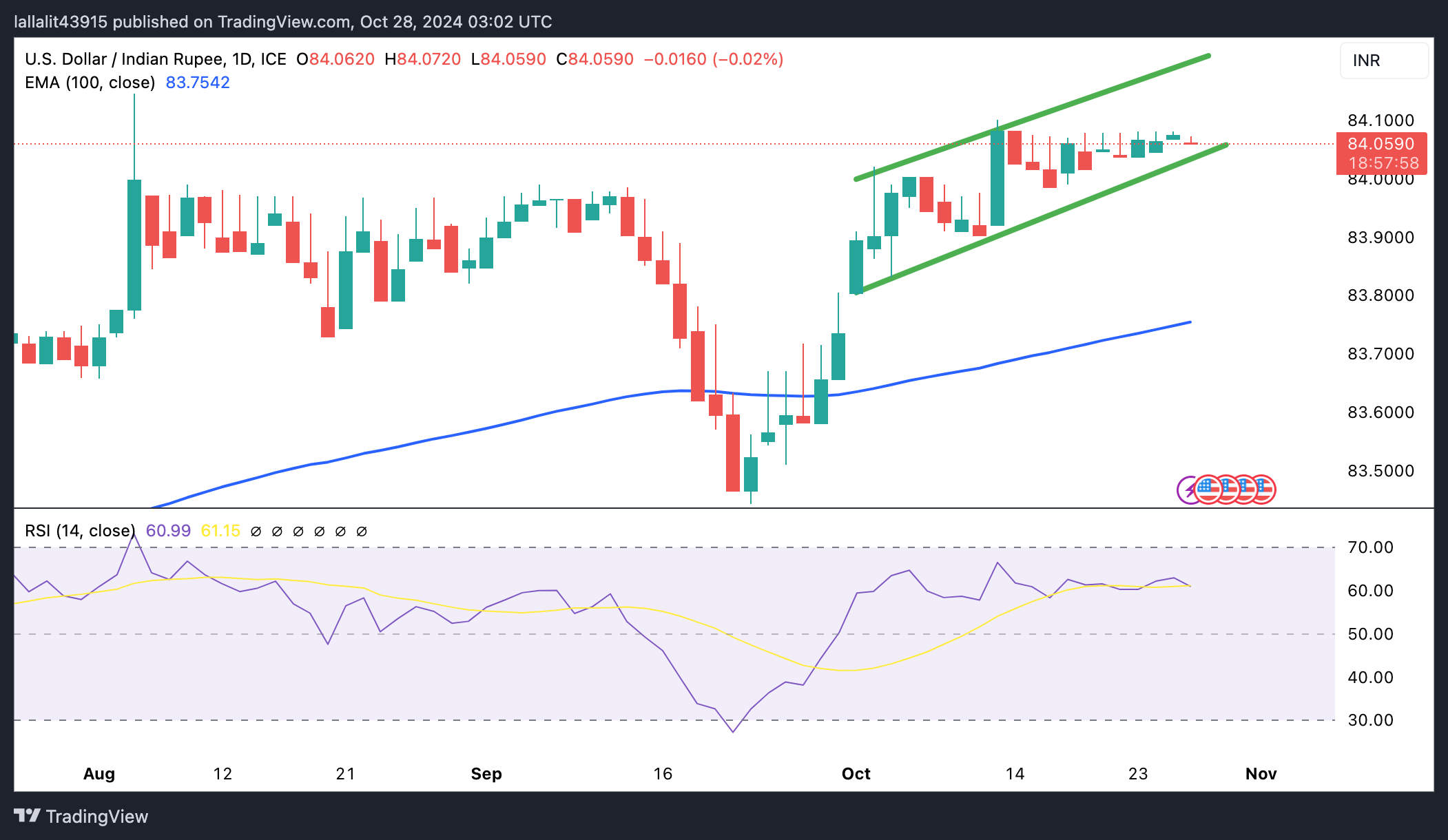
Technical Analysis: USD/INR’s constructive outlook remains in play
The Indian Rupee trades sideways on the day. According to the daily chart, the bullish
RBI FAQs
The role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in its own words, is “..to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.” This involves maintaining the inflation rate at a stable 4% level primarily using the tool of interest rates. The RBI also maintains the exchange rate at a level that will not cause excess volatility and problems for exporters and importers, since India’s economy is heavily reliant on foreign trade, especially Oil.
The RBI formally meets at six bi-monthly meetings a year to discuss its monetary policy and, if necessary, adjust interest rates. When inflation is too high (above its 4% target), the RBI will normally raise interest rates to deter borrowing and spending, which can support the Rupee (INR). If inflation falls too far below target, the RBI might cut rates to encourage more lending, which can be negative for INR.
Due to the importance of trade to the economy, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in FX markets to maintain the exchange rate within a limited range. It does this to ensure Indian importers and exporters are not exposed to unnecessary currency risk during periods of FX volatility. The RBI buys and sells Rupees in the spot market at key levels, and uses derivatives to hedge its positions.
