USD/INR edges higher on Trump’s tariff plans
- The Indian Rupee weakens in Wednesday’s Asian session.
- Trump’s tariff threats undermine the INR, but significant inflows and RBI intervention might cap its downside.
- The US Core PCE inflation data will be closely watched.
The Indian Rupee (INR) extends its decline on Wednesday. The expectation that Donald Trump might impose high tariffs on imports into the US provides some support to the US Dollar (USD) and weighs on the local currency. Additionally, the cautious stance from the Federal Reserve (Fed) could underpin the USD in the near term.
Nonetheless, the foreign inflows related to the rejig of MSCI’s global equity indexes might help limit the INR’s losses. The downside of the Indian Rupee might be capped as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) might intervene in the foreign exchange market to prevent the INR from depreciating. The US Core Personal Consumption Expenditures (Core PCE) – Price Index for October will be the highlight on Wednesday. Also, the weekly Initial Jobless Claims, Pending Home Sales, the Chicago PMI and Durable Goods Orders will be published.
Indian Rupee remains weak despite MSCI Index rebalancing
- The MSCI index rebalancing significantly boosted the Indian stock market, drawing in foreign investors who fueled over $1 billion in net purchases.
- A major portion of the Indian economy is witnessing an upward trend despite fluctuations, according to HSBC Global Research.
- Donald Trump said early Tuesday that he would announce a 25% tariff on all products from Mexico and Canada from his first day in office and impose an extra 10% tariff on goods from China.
- Minutes from the Federal Open Market Committee’s (FOMC) latest meeting indicated that the policymakers are taking a cautious approach to cutting interest rates as inflation is easing and the labor market remains strong.
- Financial markets are now pricing in nearly 57.7% possibility that the Fed will cut rates by a quarter point, down from around 69.5% a month ago, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
USD/INR holds a bullish undertone
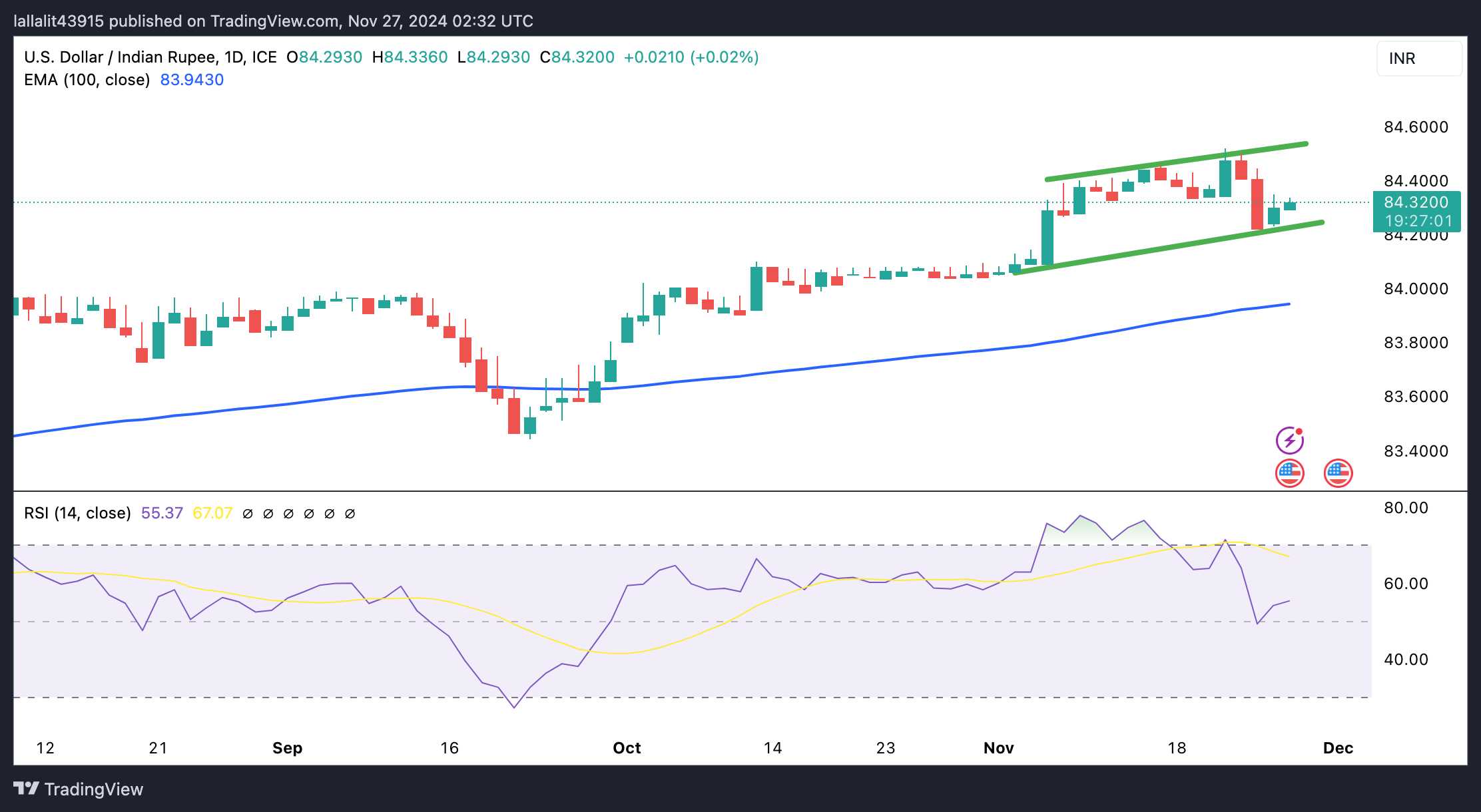
The Indian Rupee trades weaker on the day. The USD/INR pair keeps the bullish vibe within an ascending trend channel on the daily chart, with the price holding above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The upward momentum is supported by the 14-day Relative Strength Index, which is located above the midline near 55.30, suggesting further upside looks favorable.
The crucial resistance level emerges in the 84.50-84.55 zone, representing the all-time high and the upper boundary of the trend channel. Sustained bullish momentum above this level could see a rally to the 85.00 psychological mark.
On the other hand, the lower limit of the trend channel of 84.24 acts as an initial support level for USD/INR. The next contention level is seen at 83.94, the 100-day EMA. The additional downside filter to watch is 83.65, the low of August 1.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
