US Dollar softer with markets cautious on year-end period
- The US Dollar trades stable in very calm holiday trading on Friday.
- Monthly Industrial Production in Japan fell by 2.3%, less than the expected 3.5%, while big Chinese manufacturers also reported falling profits.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) briefly slipt below 108.00, remains close to a two-year high.
The US Dollar (USD) is trading a touch softer this Friday, with the DXY index unable to hold position above 108.00, as markets remain cautious and trading desks are short-staffed due to the Christmas holiday. The Dollar failed to react to more action in Asian markets, with data signaling further contraction in Japan’s Industrial Production and Chinese industrial companies reporting lower profits.
The US economic calendar is very light on Friday, with the preliminary Goods Trade Balance and the Wholesale Inventories data. Not much movement is expected from these data points. So a rather steady trading session is expected.
Daily digest market movers: Nobody taking stake
- Both data points from the US for this Friday will be released:
- The November Goods Trade Balance saw a widening deficit of 102.9 billion USD against the previous 98.7 billion USD deficit and beating the 100.8 billion USD estimate.
- November Wholesale Inventories shrunk by 0.2% against the previous 0.2% and concensus estimate.
- Equities trade mixed on Friday, with all US equity futures trading in the red before the opening bell.
- The CME FedWatch Tool for the first Fed meeting of 2025 on January 29 sees an 89.3% chance for a stable policy rate against a small 10.7% chance for a 25 basis points rate cut.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 4.59%, not far from this week’s high at 4.64%.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Nothing until January
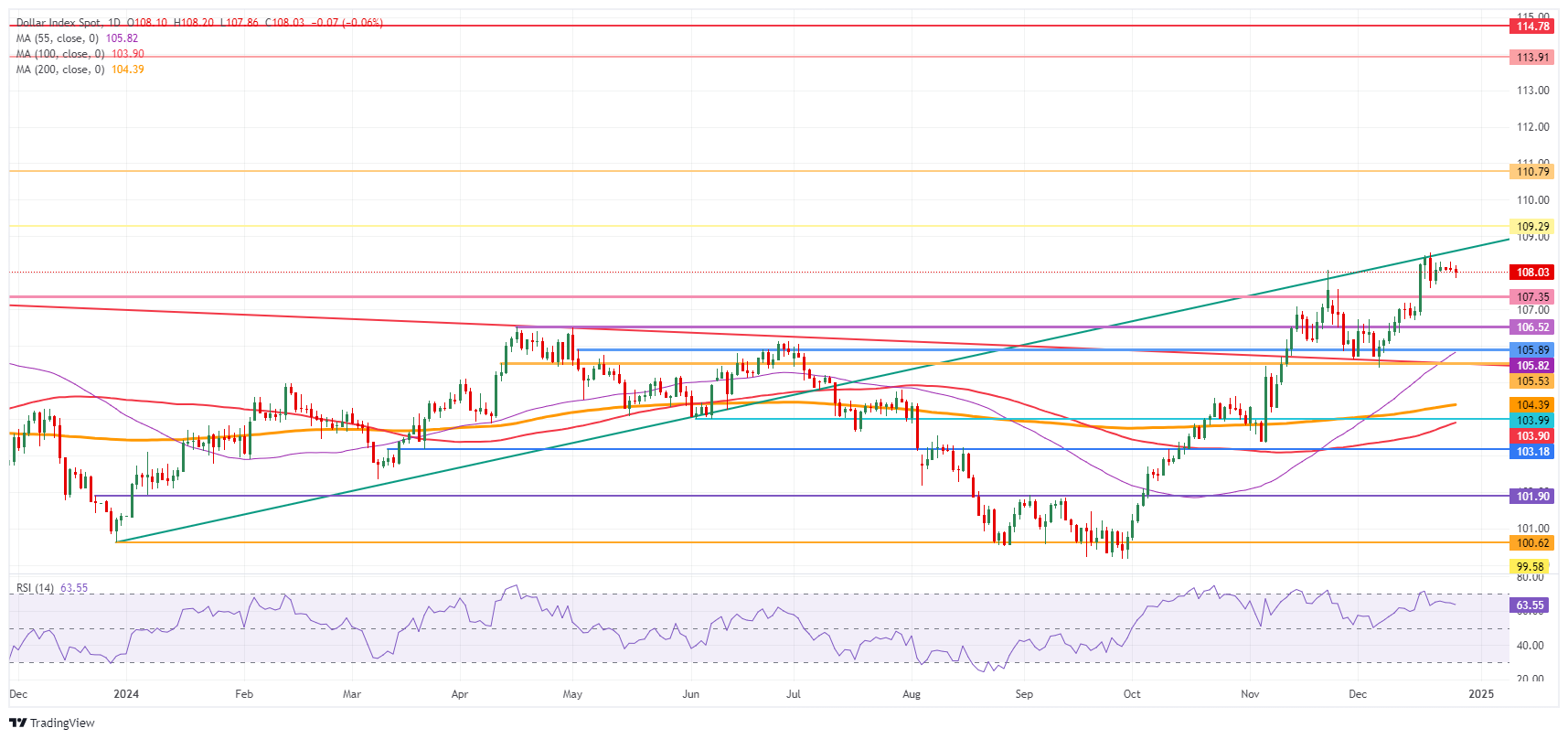
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is not expected to attack any firm levels this Friday given the low liquidity and only a handful of market participants present between Christmas and New Year. Any big movements aren’t expected unless an outside event takes place on the geopolitical front. It looks like the DXY will head into New Year’s Eve trading just above 108.00.
On the upside, a trend line originating from December 28, 2023, is acting as a moving cap. The next firm resistance comes in at 109.29, which was the peak of July 14, 2022, and has a good track record as a pivotal level. Once that level is surpassed, the 110.00 round level comes into play.
The first downside barrier comes in at 107.35, which has now turned from resistance into support. The second level that might be able to halt any selling pressure is 106.52. From there, even 105.53 could come under consideration while the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 105.83 is making its way up to that level.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.
