GBP/USD churns in congestion zone ahead of midweek holiday
- GBP/USD coiled in familiar territory just above 1.2500 on Monday.
- A lack of notable data on the UK side will constrain already-thin Cable flows.
- Broader market volumes remain tepid as investors take the year-end off.
GBP/USD pulled back on Monday, kicking off the new trading week with a fresh down day. The pair fell around one-third of one percent, easing back below 1.2550 as bids remain mired in a near-term congestion pattern on the bottom end of recent price action. The UK’s data release schedule this week is devoid of any meaningful prints, leaving Cable at the mercy of broader market flows in a tepid year-end environment.
Outside of some general profit-taking and long-term position management, global market volumes are crimped tightly by the year-end holiday season. Markets will be further constrained in the midweek, when global markets will be shuttered for the New Year’s Day closure.
This week, the main data highlight will be the December US ISM PMI figures, set to be released on Friday. The December US ISM Manufacturing PMI is projected to decrease slightly to 48.3 from 48.4. Additionally, several Federal Reserve (Fed) officials are scheduled to speak during the latter part of the week, as they work to clarify the Fed’s recent shift towards lower-than-expected projections for the number of rate cuts anticipated in 2024.
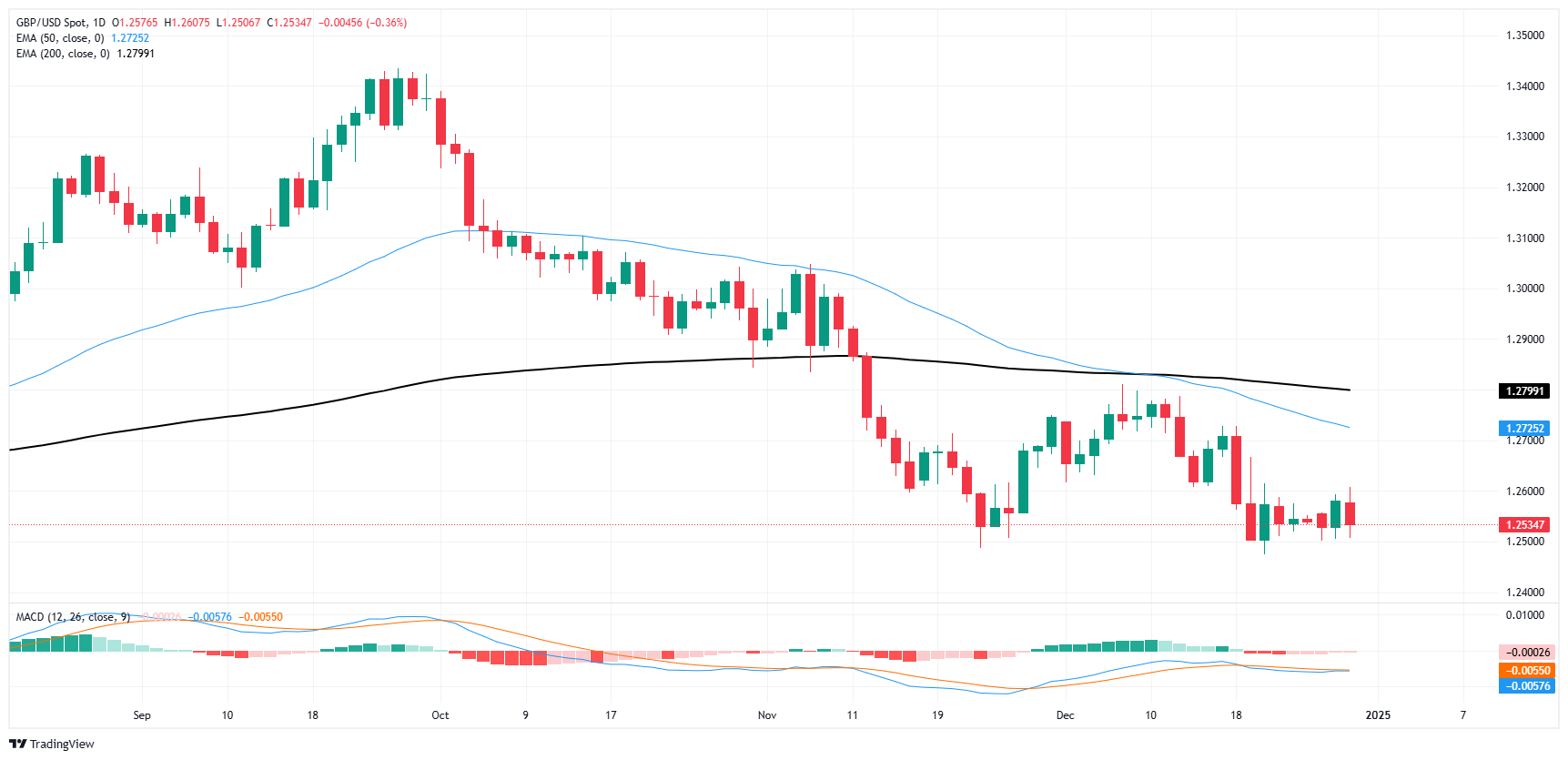
GBP/USD price forecast
With Cable price action continuing to grind out chart paper just above 1.2500, GBP/USD is sliding into a sideways channel in the near-term. However, Cable traders should be on the lookout for a fast breakout to either side once the new year kicks off in earnest.
GBP/USD hasn’t made much progress to the low side after hitting multi-month lows in November, however a bullish recovery fizzled before bids could challenge the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) which is now falling through 1.2800.
GBP/USD daily chart
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
