Japanese Yen steadies against US Dollar due to post-New Year light trading
- The Japanese Yen gains ground as traders expect the BoJ to deliver an interest rate hike in January.
- Japan’s Jibun Bank Manufacturing PMI reached 49.6 in December, exceeding the expected 49.5 and prior 49.0 readings.
- The US Dollar remains subdued as US Treasury yields decline, with the 2- and 10-year at 4.32% and 4.62%, respectively.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) remains stronger against the US Dollar (USD) on Monday. The USD/JPY pair remains subdued as the Japanese Yen (JPY) strengthens on the likelihood of the Bank of Japan (BoJ) raising interest rates in January following the release of Tokyo Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation data last week.
Japan’s Jibun Bank Manufacturing PMI reached 49.6 in December, slightly exceeding the flash estimate of 49.5 and improving from 49.0 in November. Although it marked the highest level since September, it still signaled the sixth consecutive month of declining factory activity.
The Nikkei 225 fell to around 39,950 on Monday, snapping two days of gains. The decline came after a slight drop in US futures, following Friday’s Wall Street slump driven by rising Treasury yields and indications of more restrained interest rate cuts in 2025.
Japanese Yen holds minor gains as US Dollar edges lower amid subdued Treasury yields
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the value of the US Dollar (USD) against its six major peers, trades around 108.00. The Greenback faces challenges as US Treasury bond yields depreciate on Monday. 2-year and 10-year yields stand at 4.32% and 4.62%, respectively, at the time of writing.
- The US Dollar may gain support from growing expectations of fewer rate cuts next year by the US Federal Reserve (Fed). Traders continue to digest the Fed’s hawkish pivot. The Fed cut its benchmark interest rate by a quarter point at the December meeting, and the latest Dot Plots indicated two rate cuts next year.
- The headline Tokyo CPI inflation rose to 3.0% YoY in December, up from 2.6% in November. Meanwhile, the Tokyo CPI excluding Fresh Food and Energy increased to 2.4% YoY in December, compared to 2.2% the previous month. The Tokyo CPI excluding Fresh Food also climbed 2.4% YoY in December, slightly below the expected 2.5% but higher than the 2.2% recorded in November.
- On Friday, Japan’s Finance Minister Katsunobu Kato said that he recently saw one-sided and sharp foreign exchange (FX) moves. Kato further stated that the official will take suitable measures against excessive foreign exchange movements.
- The Bank of Japan (BoJ) released the Summary of Opinions from its December monetary policy meeting on Friday, highlighting plans to adjust easing measures if economic conditions align with expectations. One BoJ board member emphasized the importance of monitoring wage negotiation momentum, while another stressed the need for scrutiny of data to determine any changes to monetary support.
- The Bank of Japan October meeting Minutes released this Tuesday reiterated the possibility of gradual rate hikes if inflation trends align with expectations, with a potential path to 1.0% by late fiscal 2025. The Minutes also emphasized a cautious approach to monetary policy, wage-driven economic growth amid domestic and global uncertainties, and fiscal measures to counter deflationary pressures.
- Earlier in the month, BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda said that the central bank expects the Japanese economy to move closer to sustainably achieving the BoJ’s 2% inflation target next year. Ueda also added, “The timing and pace of adjusting the degree of monetary accommodation will depend on developments in economic activity and prices as well as financial conditions going forward.”
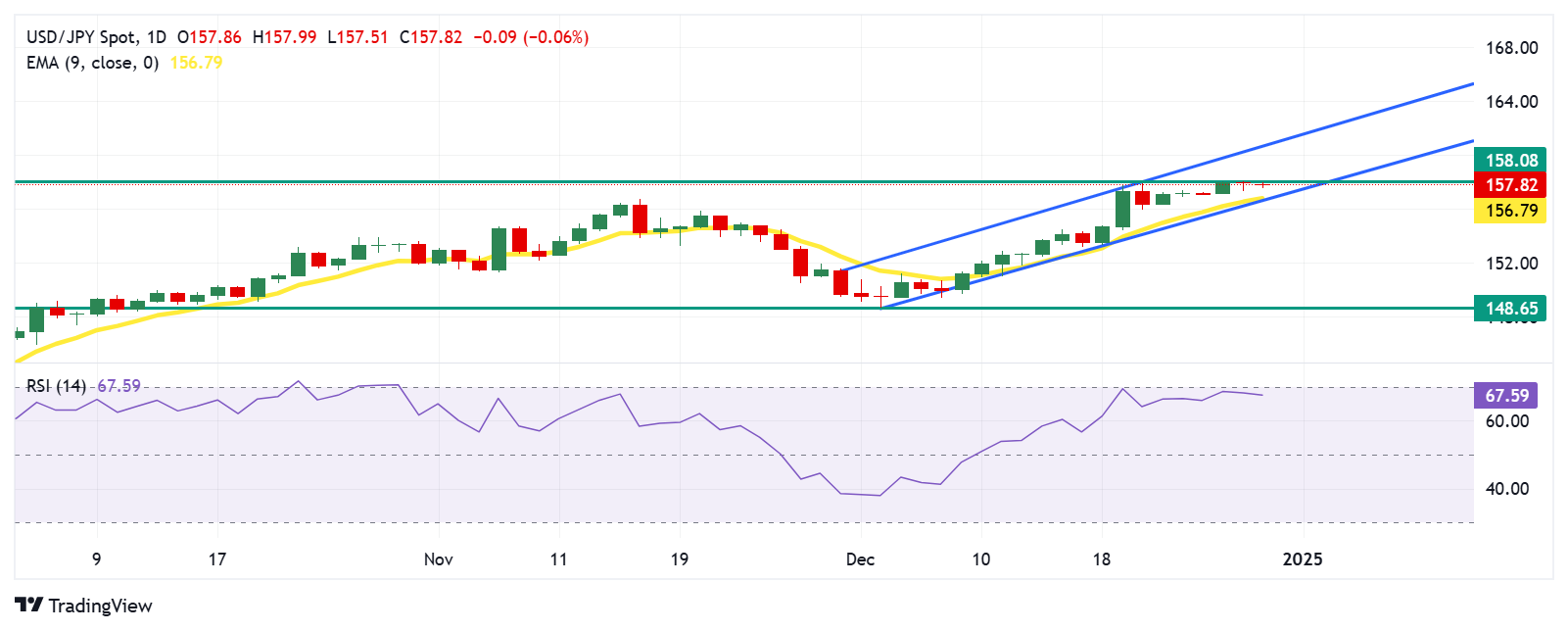
Technical Analysis: USD/JPY remains subdued below monthly highs near 158.00
The USD/JPY pair trades near 157.80 on Monday, maintaining its bullish momentum within an ascending channel on the daily chart. The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) hovers just below the 70 level, supporting the bullish trend. However, if the RSI surpasses the 70 mark, it could indicate an overbought condition, potentially triggering a downward correction.
On the upside, the USD/JPY pair may retest its monthly high of 158.08, reached on December 26. A decisive break above this level could pave the way for further gains, with the pair potentially targeting the ascending channel’s upper boundary near 160.60.
The immediate support lies at the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 156.79, closely aligned with the ascending channel’s lower boundary near 156.50.
USD/JPY: Daily Chart
Japanese Yen PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of Japanese Yen (JPY) against listed major currencies today. Japanese Yen was the strongest against the Swiss Franc.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.01% | -0.05% | 0.09% | -0.16% | -0.42% | -0.51% | 0.02% | |
| EUR | 0.00% | -0.04% | 0.08% | -0.20% | -0.48% | -0.54% | -0.02% | |
| GBP | 0.05% | 0.04% | 0.14% | -0.15% | -0.44% | -0.50% | 0.02% | |
| JPY | -0.09% | -0.08% | -0.14% | -0.28% | -0.47% | -0.46% | -0.05% | |
| CAD | 0.16% | 0.20% | 0.15% | 0.28% | -0.27% | -0.28% | 0.17% | |
| AUD | 0.42% | 0.48% | 0.44% | 0.47% | 0.27% | -0.06% | 0.46% | |
| NZD | 0.51% | 0.54% | 0.50% | 0.46% | 0.28% | 0.06% | 0.52% | |
| CHF | -0.02% | 0.02% | -0.02% | 0.05% | -0.17% | -0.46% | -0.52% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Japanese Yen from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the US Dollar, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent JPY (base)/USD (quote).
Bank of Japan FAQs
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) is the Japanese central bank, which sets monetary policy in the country. Its mandate is to issue banknotes and carry out currency and monetary control to ensure price stability, which means an inflation target of around 2%.
The Bank of Japan embarked in an ultra-loose monetary policy in 2013 in order to stimulate the economy and fuel inflation amid a low-inflationary environment. The bank’s policy is based on Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE), or printing notes to buy assets such as government or corporate bonds to provide liquidity. In 2016, the bank doubled down on its strategy and further loosened policy by first introducing negative interest rates and then directly controlling the yield of its 10-year government bonds. In March 2024, the BoJ lifted interest rates, effectively retreating from the ultra-loose monetary policy stance.
The Bank’s massive stimulus caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers. This process exacerbated in 2022 and 2023 due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks, which opted to increase interest rates sharply to fight decades-high levels of inflation. The BoJ’s policy led to a widening differential with other currencies, dragging down the value of the Yen. This trend partly reversed in 2024, when the BoJ decided to abandon its ultra-loose policy stance.
A weaker Yen and the spike in global energy prices led to an increase in Japanese inflation, which exceeded the BoJ’s 2% target. The prospect of rising salaries in the country – a key element fuelling inflation – also contributed to the move.
