Japanese Yen bulls seem reluctant amid BoJ uncertainty
- The Japanese Yen meets with a fresh supply during the Asian session amid mixed BoJ rate hike cues.
- A positive risk tone further undermines the safe-haven JPY, though the downside seems cushioned.
- Rising Fed rate cut bets should cap any USD recovery and contribute to capping the USD/JPY pair.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) drifts lower during the Asian session on Friday after the Summary of Opinions from the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) July meeting showed that policymakers remain worried about the US tariffs uncertainty. Adding to this, receding safe-haven demand turns out to be another factor undermining the JPY. This, along with the emergence of some US Dollar (USD) buying, assists the USD/JPY pair to rebound from the 146.70 pivotal support.
Meanwhile, the BoJ last week opened the door for an imminent rate hike by the end of this year. This marks a significant divergence in comparison to the growing acceptance that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will resume its rate-cutting cycle in September. The Fed’s dovish outlook might cap the USD recovery and support the lower-yielding JPY. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for strong follow-through buying before placing fresh bullish bets around the USD/JPY pair.
Japanese Yen sticks to negative bias amid positive risk tone, BoJ rate hike uncertainty
- The Bank of Japan published the Summary of Opinions of its July 30-31 meeting earlier this Friday, which showed that board members maintained their view for further interest-rate increases despite high uncertainty over tariffs. The summary further revealed that Japan’s economic growth will moderate, and the improvement in underlying inflation will be sluggish temporarily.
- Earlier, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications reported that Japan’s Household Spending rose in June at a slower rate than expected as higher prices added pressure to broader consumption trends. Consumer spending fell 5.2% on a monthly basis, marking the steepest decline since January 2021, suggesting that prospects for BoJ rate hikes could be delayed further.
- Japan’s Topix index rose above the 3000 psychological mark for the first time ever, while the tech-focused Nikkei 225 rallied to its highest since July 25. This, in turn, prompts some selling around traditional safe-haven assets, including the Japanese Yen. Apart from this, a modest US Dollar recovery assists the USD/JPY pair to rebound around 60-70 pips from the Asian session low.
- Any meaningful USD appreciation, however, seems elusive amid bets that the Federal Reserve will resume its rate-cutting cycle in September. The expectations were reaffirmed by the US Weekly Initial Jobless Claims data released on Thursday, which rose more than expected last week to the highest level in a month. This further pointed to signs of a cooling US labor market.
- Moreover, concerns about the Fed’s independence might contribute to capping gains for the USD and the USD/JPY pair. Meanwhile, US President Donald Trump nominated Council of Economic Advisers Chairman Stephen Miran to serve out the rest of Fed Governor Adriana Kugler’s term and has short-listed four candidates as replacements for Fed Chair Jerome Powell.
- Moving ahead, there isn’t any relevant market-moving economic data due for release from the US on Friday, leaving the USD at the mercy of speeches from influential FOMC members. Apart from this, the broader risk sentiment could provide some impetus heading into the weekend. Nevertheless, the mixed fundamental backdrop warrants caution for aggressive USD/JPY traders.
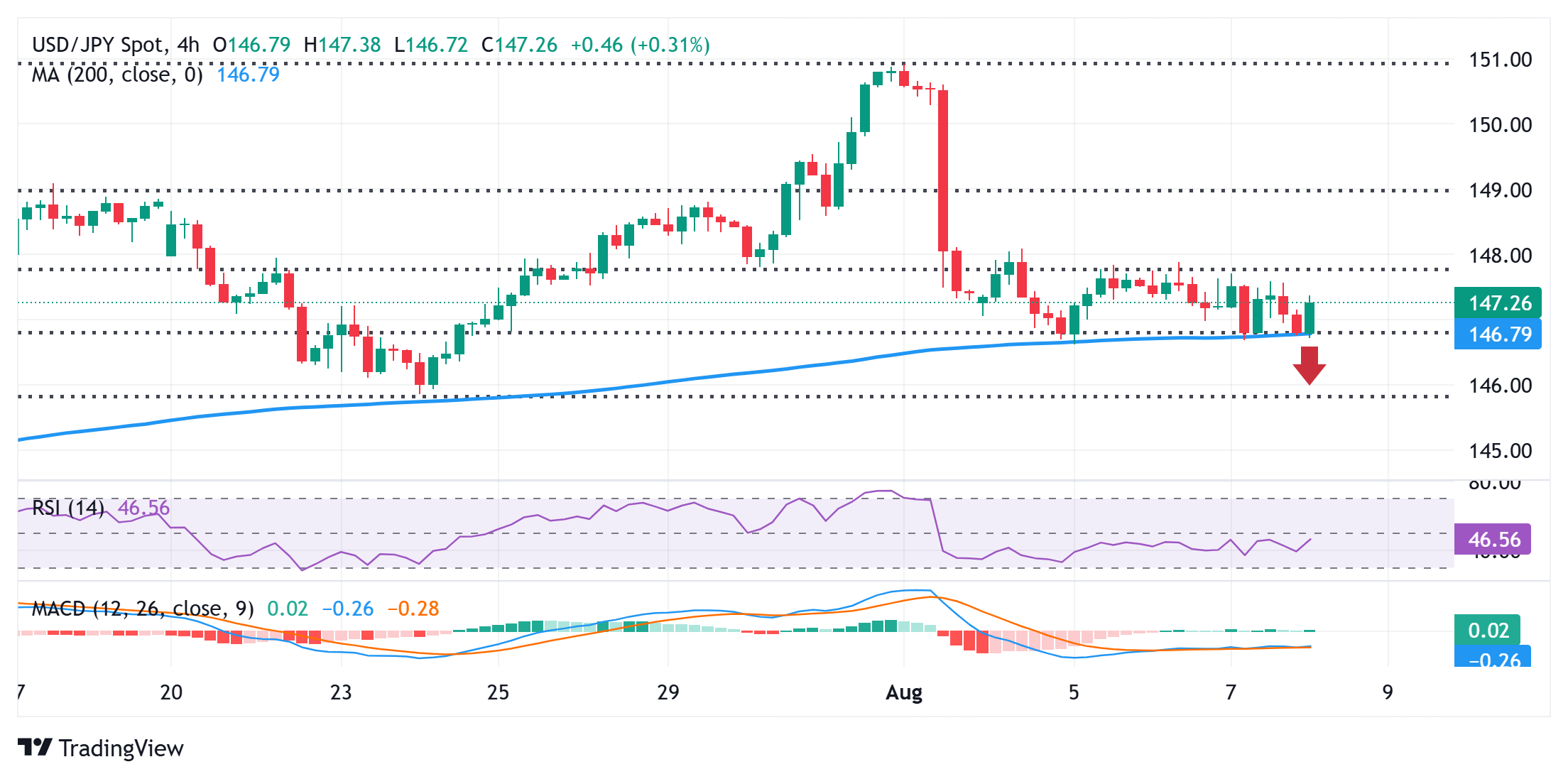
USD/JPY could climb further once 38.2% Fibo. level near 147.75-147.80 is cleared
From a technical perspective, spot prices remain confined in the weekly trading band. Against the backdrop of last week’s sharp pullback from the 151.00 neighborhood, or the highest level since March 28, the range-bound price action might still be categorized as a bearish consolidation phase. Moreover, slightly negative oscillators on the daily chart suggest that the path of least resistance for the USD/JPY pair is to the downside.
Hence, any further move up might continue to attract fresh sellers and remain capped near the 147.75-147.80 region, representing the 38.2% Fibonacci retracement level of the upswing in July. That said, some follow-through buying, leading to a subsequent strength beyond the 148.00 mark, could lift the USD/JPY pair to the 148.45-148.50 region. The momentum could extend further towards the 23.6% Fibo. retracement level, just ahead of the 149.00 mark.
On the flip side, the 146.75-146.70 confluence – comprising the 200-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) on the 4-hour and the 50% Fibo. retracement level – might continue to protect the immediate downside. A convincing break below should pave the way for deeper losses and drag the USD/JPY pair to sub-146.00 levels, or the 61.8% Fibo. retracement level. Some follow-through selling below the latter could expose the 145.00 psychological mark.
Risk sentiment FAQs
In the world of financial jargon the two widely used terms “risk-on” and “risk off” refer to the level of risk that investors are willing to stomach during the period referenced. In a “risk-on” market, investors are optimistic about the future and more willing to buy risky assets. In a “risk-off” market investors start to ‘play it safe’ because they are worried about the future, and therefore buy less risky assets that are more certain of bringing a return, even if it is relatively modest.
Typically, during periods of “risk-on”, stock markets will rise, most commodities – except Gold – will also gain in value, since they benefit from a positive growth outlook. The currencies of nations that are heavy commodity exporters strengthen because of increased demand, and Cryptocurrencies rise. In a “risk-off” market, Bonds go up – especially major government Bonds – Gold shines, and safe-haven currencies such as the Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc and US Dollar all benefit.
The Australian Dollar (AUD), the Canadian Dollar (CAD), the New Zealand Dollar (NZD) and minor FX like the Ruble (RUB) and the South African Rand (ZAR), all tend to rise in markets that are “risk-on”. This is because the economies of these currencies are heavily reliant on commodity exports for growth, and commodities tend to rise in price during risk-on periods. This is because investors foresee greater demand for raw materials in the future due to heightened economic activity.
The major currencies that tend to rise during periods of “risk-off” are the US Dollar (USD), the Japanese Yen (JPY) and the Swiss Franc (CHF). The US Dollar, because it is the world’s reserve currency, and because in times of crisis investors buy US government debt, which is seen as safe because the largest economy in the world is unlikely to default. The Yen, from increased demand for Japanese government bonds, because a high proportion are held by domestic investors who are unlikely to dump them – even in a crisis. The Swiss Franc, because strict Swiss banking laws offer investors enhanced capital protection.
