Australian Dollar remains steady after recovering losses, US GDP Annualized eyed
- The Australian Dollar recovers daily losses after the release of Consumer Inflation Expectations on Thursday.
- Australia’s Consumer Inflation Expectations increased to 4.2% in December from the previous 3.8% rise.
- US Dollar surged as the Fed delivered a hawkish cut of 25 basis points at its December meeting.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) pares daily losses following the release of Consumer Inflation Expectations on Thursday. However, the AUD/USD pair declined as the US Dollar (USD) appreciated as the Federal Reserve (Fed) delivered a hawkish cut of 25 basis points (bps) at its December meeting on Wednesday, bringing its benchmark lending rate to a range of 4.25%-4.50%, a two-year low.
Australia’s Consumer Inflation Expectations rose to 4.2% in December from 3.8% in the previous month, marking the highest level since September. However, the AUD struggles due to the increased likelihood that the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) will cut interest rates sooner and more significantly than initially expected. However, future decisions will be data-driven, with evolving risk assessments guiding the RBA’s approach.
The US Dollar appreciated as the Summary of Economic Projections, or ‘dot-plot,’ showed only two rate cuts in 2025, down from the four they projected in September. Additionally, during the Press Conference, Fed Chair Jerome Powell made clear that the Fed will be cautious about further cuts as inflation remains stubbornly above the central bank’s 2% target.
Traders will likely observe the US weekly Initial Jobless Claims, Existing Home Sales, and final reading of Gross Domestic Product Annualized for the third quarter (Q3) due on Thursday.
Australian Dollar receives downward pressure following Fed’s hawkish rate cut
- National Australia Bank (NAB) maintains its forecast for the first Reserve Bank of Australia rate cut at the May 2025 meeting, though they acknowledge February as a possibility. NAB’s report indicates that the Unemployment Rate is expected to peak at 4.3% before easing to 4.2% by 2026 as the economy stabilizes. The Q4 trimmed mean inflation is projected at 0.6% quarter-on-quarter, with a gradual easing expected, reaching 2.7% by late 2025.
- Australia’s Westpac Consumer Confidence fell 2% to 92.8 points in December, reversing two months of positive momentum.
- On Tuesday, the US Census Bureau reported that US Retail Sales rose 0.7% MoM in November, compared to the 0.5% prior increase. Meanwhile, the Retail Sales Control Group increased 0.4% from the previous decline of 0.1%.
- Reuters cited two sources on Tuesday that China is set to target economic growth of around 5% in 2025. This decision follows a meeting among top Chinese officials at the Central Economic Work Conference last week. The growth target remains the same as this year, which China is expected to achieve.
- China’s foreign exchange regulator, the State Administration of Foreign Exchange (SAFE), reported a net outflow of $45.7 billion from China’s capital markets in November. Cross-border portfolio investment receipts totaled $188.9 billion, while payments reached $234.6 billion, resulting in the largest monthly deficit on record for this category.
- The preliminary S&P Global US Composite Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) rose to 56.6 in December, from 54.9 prior. Meanwhile, the Services PMI improved to 58.5 from 56.1. The Manufacturing PMI declined to 48.3 in December, from the previous 49.7 reading.
- Chinese authorities, led by President Xi Jinping, have pledged to raise the fiscal deficit target next year, shifting policy focus to consumption to boost the economy amid looming 10% US tariffs threatening exports. The lack of concrete details on fiscal support has put downward pressure on the AUD, given China’s status as Australia’s largest trading partner.
Australian Dollar holds position above 0.6200, descending channel’s lower boundary
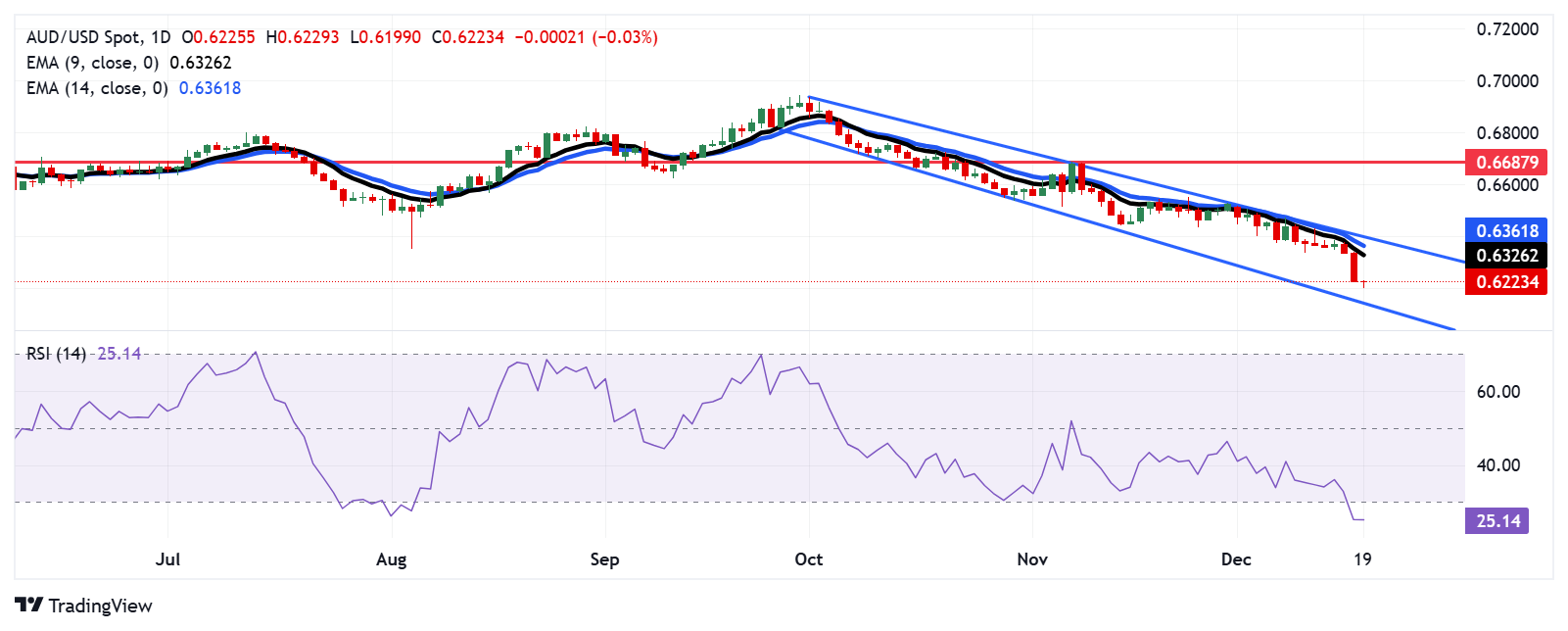
The AUD/USD pair trades near 0.6220 on Thursday. Analysis of a daily chart suggests a prevailing bearish bias as the pair moves downwards within a descending channel pattern. However, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) has broken below the 30 level, indicating an oversold situation and a potential for an upward correction soon.
Regarding support, the AUD/USD pair could navigate the descending channel’s lower boundary around the 0.6140 level.
On the upside, the AUD/USD pair may find its initial resistance around the nine-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 0.6326, followed by the 14-day EMA at 0.6362, aligned with the descending channel’s upper boundary at 0.6400 level. A decisive breakout above this channel could drive the pair toward the eight-week high at 0.6687.
AUD/USD: Daily Chart
US Dollar PRICE Today
The table below shows the percentage change of US Dollar (USD) against listed major currencies today. US Dollar was the strongest against the New Zealand Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | JPY | CAD | AUD | NZD | CHF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USD | -0.10% | -0.10% | -0.05% | 0.04% | 0.00% | 0.63% | -0.07% | |
| EUR | 0.10% | 0.00% | 0.02% | 0.14% | 0.11% | 0.74% | 0.03% | |
| GBP | 0.10% | -0.00% | 0.04% | 0.14% | 0.11% | 0.74% | 0.03% | |
| JPY | 0.05% | -0.02% | -0.04% | 0.12% | 0.07% | 0.67% | -0.00% | |
| CAD | -0.04% | -0.14% | -0.14% | -0.12% | -0.03% | 0.57% | -0.11% | |
| AUD | -0.00% | -0.11% | -0.11% | -0.07% | 0.03% | 0.63% | -0.07% | |
| NZD | -0.63% | -0.74% | -0.74% | -0.67% | -0.57% | -0.63% | -0.70% | |
| CHF | 0.07% | -0.03% | -0.03% | 0.00% | 0.11% | 0.07% | 0.70% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the US Dollar from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent USD (base)/JPY (quote).
Australian Dollar FAQs
One of the most significant factors for the Australian Dollar (AUD) is the level of interest rates set by the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA). Because Australia is a resource-rich country another key driver is the price of its biggest export, Iron Ore. The health of the Chinese economy, its largest trading partner, is a factor, as well as inflation in Australia, its growth rate and Trade Balance. Market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – is also a factor, with risk-on positive for AUD.
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) influences the Australian Dollar (AUD) by setting the level of interest rates that Australian banks can lend to each other. This influences the level of interest rates in the economy as a whole. The main goal of the RBA is to maintain a stable inflation rate of 2-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively high interest rates compared to other major central banks support the AUD, and the opposite for relatively low. The RBA can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former AUD-negative and the latter AUD-positive.
China is Australia’s largest trading partner so the health of the Chinese economy is a major influence on the value of the Australian Dollar (AUD). When the Chinese economy is doing well it purchases more raw materials, goods and services from Australia, lifting demand for the AUD, and pushing up its value. The opposite is the case when the Chinese economy is not growing as fast as expected. Positive or negative surprises in Chinese growth data, therefore, often have a direct impact on the Australian Dollar and its pairs.
Iron Ore is Australia’s largest export, accounting for $118 billion a year according to data from 2021, with China as its primary destination. The price of Iron Ore, therefore, can be a driver of the Australian Dollar. Generally, if the price of Iron Ore rises, AUD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Iron Ore falls. Higher Iron Ore prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance for Australia, which is also positive of the AUD.
The Trade Balance, which is the difference between what a country earns from its exports versus what it pays for its imports, is another factor that can influence the value of the Australian Dollar. If Australia produces highly sought after exports, then its currency will gain in value purely from the surplus demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase its exports versus what it spends to purchase imports. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens the AUD, with the opposite effect if the Trade Balance is negative.
