US Dollar Index faces first meltdown just hours before Trump returns to office
- The US Dollar undergoes a small melt down as headlines are being issued on President Trump’s first actions.
- The WSJ confirms that tariffs need to be further discussed before being issued.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) snaps 109.00 and heads towards 108.00
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, is sinking 1% just hours ahead of President-elect Donald Trump’s inauguration as the 47th President of the United States (US). Several asset classes in the US will remain closed, such as the Wall Street trading floor and US bond trading, in observance of Martin Luther King’s Day. The first seismic shock in the DXY comes after headlines emerged form the Wall Street Journal that tariffs are not a part of the executive orders that President Donald Trump will issue on his first day in office, and need to be discussed further before being implemented.
All eyes will be on the aftermath of the inauguration, where President-elect Donald Trump has already confirmed in a rally on Sunday that a whole battery of new measures and executive orders will be issued. The main ones are, of course, more tariffs, mass deportation starting in Chicago, and issuing state of emergencies for energy and border security, Bloomberg reported. By issuing those last two, the upcoming President Trump can give the green light for massive drilling and mass deporting illegal immigrants without having to pass through Congress and the House of Representatives.
Daily digest market movers: Tariffs softer
- The Wall Street Journal issues a headline that confirms the Trump administration to form a task group first to discuss proper impacts from tariffs on China, Canada and Mexico before considering to issue them.
- At 17:00 GMT, the Presidential Inauguration will take place, with Donald Trump being sworn in as the 47th President of the United States.
- Due to Martin Luther King’s Day, several trading floors in the US will remain closed throughout the day.
- Equities are very happy with the softer US Dollar. All European equities and US futures are off to a good start for this week.
- The CME FedWatch tool projects a 55.6% chance that interest rates will remain unchanged at current levels in the May meeting, suggesting a rate cut in June. Expectations are that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will remain data-dependent with uncertainties that could influence inflation during President-elect Donald Trump’s term.
- The US 10-year yield is trading around 4.627% and will remain at that level this Monday, as bond trading in the US is closed due to the Martin Luther King’s bank holiday.
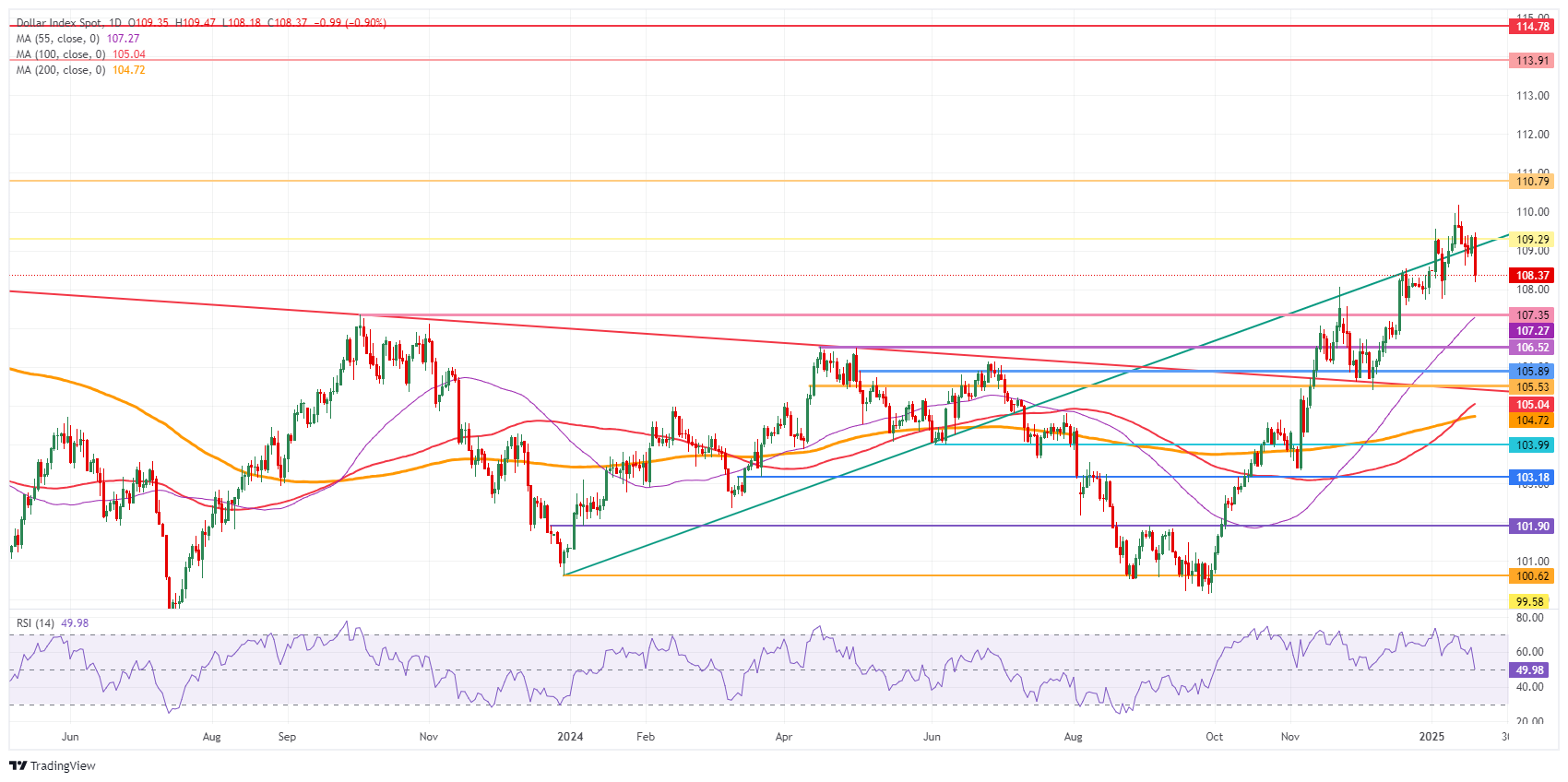
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: That is just the beginning.
The US Dollar Index (DXY) sees a split division between bears and bulls. The new Trump administration is set to unleash a large number of executive orders, making it hard for markets to assess the impact. With several topics being addressed and communicated in advance, it looks like markets have already priced in a fair bit of inflationary pressure from Trumponomics. The question now will be if the markets are correct and if the DXY index will ease further from current levels on the back of an overestimation of the actual impact of the measures being imposed.
On the upside, the 110.00 psychological level remains the key resistance to beat. Further up, the next big upside level to hit before advancing any further remains at 110.79 (September 7, 2022, high). Once beyond there, it is quite a stretch to 113.91, a double top from October 2022.
On the downside, the DXY is trading alongside the ascending trend line coming from December 2023, which currently comes in around 109.10 as nearby support. In case of more downside, the next support is 107.35 (October 3, 2023, high). Further down, the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 107.29 should catch any falling knives.
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
Central banks FAQs
Central Banks have a key mandate which is making sure that there is price stability in a country or region. Economies are constantly facing inflation or deflation when prices for certain goods and services are fluctuating. Constant rising prices for the same goods means inflation, constant lowered prices for the same goods means deflation. It is the task of the central bank to keep the demand in line by tweaking its policy rate. For the biggest central banks like the US Federal Reserve (Fed), the European Central Bank (ECB) or the Bank of England (BoE), the mandate is to keep inflation close to 2%.
A central bank has one important tool at its disposal to get inflation higher or lower, and that is by tweaking its benchmark policy rate, commonly known as interest rate. On pre-communicated moments, the central bank will issue a statement with its policy rate and provide additional reasoning on why it is either remaining or changing (cutting or hiking) it. Local banks will adjust their savings and lending rates accordingly, which in turn will make it either harder or easier for people to earn on their savings or for companies to take out loans and make investments in their businesses. When the central bank hikes interest rates substantially, this is called monetary tightening. When it is cutting its benchmark rate, it is called monetary easing.
A central bank is often politically independent. Members of the central bank policy board are passing through a series of panels and hearings before being appointed to a policy board seat. Each member in that board often has a certain conviction on how the central bank should control inflation and the subsequent monetary policy. Members that want a very loose monetary policy, with low rates and cheap lending, to boost the economy substantially while being content to see inflation slightly above 2%, are called ‘doves’. Members that rather want to see higher rates to reward savings and want to keep a lit on inflation at all time are called ‘hawks’ and will not rest until inflation is at or just below 2%.
Normally, there is a chairman or president who leads each meeting, needs to create a consensus between the hawks or doves and has his or her final say when it would come down to a vote split to avoid a 50-50 tie on whether the current policy should be adjusted. The chairman will deliver speeches which often can be followed live, where the current monetary stance and outlook is being communicated. A central bank will try to push forward its monetary policy without triggering violent swings in rates, equities, or its currency. All members of the central bank will channel their stance toward the markets in advance of a policy meeting event. A few days before a policy meeting takes place until the new policy has been communicated, members are forbidden to talk publicly. This is called the blackout period.
