Japanese Yen sticks to intraday bearish bias amid trade tensions
- The Japanese Yen continues losing ground amid worries about Trump’s trade tariffs.
- Fed’s hawkish stance revives the USD demand and lends support to the USD/JPY pair.
- Rising bets for another BoJ rate hike in March could limit any further JPY decline.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) attracts heavy selling for the third straight day on Wednesday, which, along with a modest US Dollar (USD) uptick, lifts the USD/JPY pair further beyond mid-153.00s during the Asian session. Against the backdrop of US President Donald Trump’s 25% tariffs on all US imports of steel and aluminum, concerns about broader reciprocal tariffs turn out to be a key factor behind the JPY’s underperformance.
Apart from this, a generally positive tone around the equity markets further seems to undermine the safe-haven JPY, though bets at the Bank of Japan (BoJ) raise interest rates again warrant caution for bearish traders. Meanwhile, Federal Reserve (Fed) Chair Jerome Powell’s hawkish remarks on Tuesday helped revive the USD demand and support the USD/JPY pair. Traders now look to the US consumer inflation figures for a fresh impetus.
Japanese Yen remains heavily offered amid Trump tariff uncertainties
- US President Donald Trump signed executive orders to impose 25% tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from March 12. Trump also signaled he would look at imposing additional tariffs on automobiles, pharmaceuticals, and computer chips, and promised broader reciprocal tariffs to match the levies other governments charge on US products.
- The announcement raises the risk of a further escalation of global trade tensions and threatens to negatively affect the Japanese economy. This, in turn, is seen weighing heavily on the Japanese Yen and assists the USD/JPY pair to build on a one-week-old goodish recovery move from sub-151.00 levels, or a near two-month low touched last week.
- Japan’s Finance Minister, Katsunobu Kato said earlier this Wednesday that he will assess the impact of US tariffs on the Japanese economy and respond appropriately. Separately, Japan industry minister Yoji Muto requested the US to exclude Japan from steel and aluminum tariffs. This, however, does little to provide any respite to the JPY bulls.
- Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell, in remarks before the Senate Banking Committee on Tuesday, struck a more hawkish tone and called the economy strong overall with a solid labor market. Powell added that inflation is closer to the 2% goal but still somewhat elevated and signaled that policymakers aren’t in a rush to push interest rates lower.
- Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda reiterated earlier today that the central bank will conduct monetary policy appropriately in order to achieve the 2% inflation target. Moreover, the recent wage growth data and the broadening inflationary pressures in the economy back the case for another BoJ rate hike move at the March policy meeting.
- Traders now look forward to the release of the latest US consumer inflation figures, which, along with Powell’s congressional testimony, will drive the US Dollar and the USD/JPY pair. The headline US Consumer Price Index is seen rising 2.9% YoY in January and the core CPI (excluding food and energy prices) coming in at a 3.1% YoY rate.
USD/JPY is more likely to face a stiff resistance near the 154.00 round figure
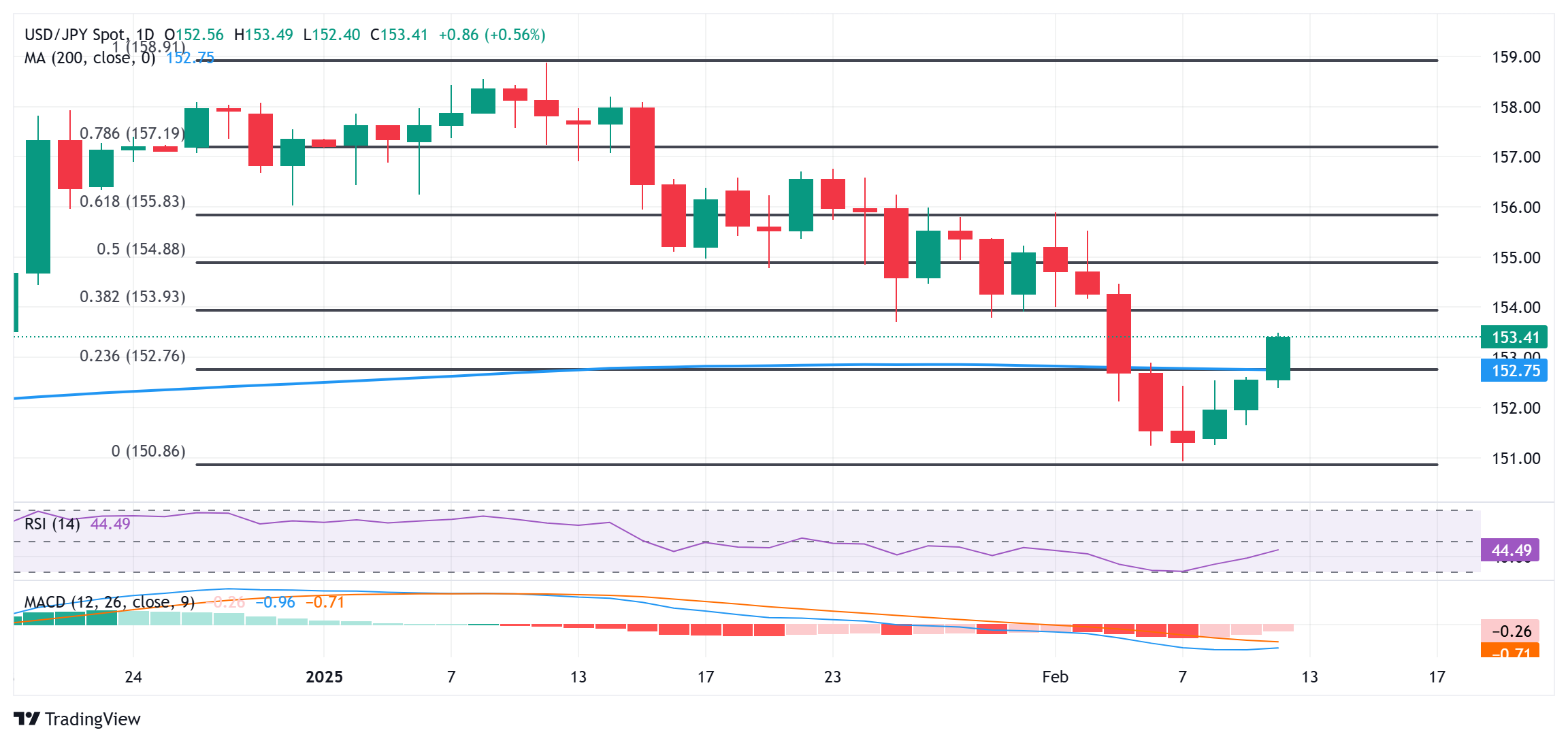
From a technical perspective, a sustained breakout above the 152.75 confluence hurdle could be seen as a key trigger for bullish traders and support prospects for a further intraday appreciating move. The said area comprises the 23.6% Fibonacci retracement level of the January-February decline, the 200-day Simple Moving Averages (SMA), which, in turn, should act as a pivotal point for the USD/JPY pair.
Meanwhile, oscillators on the daily chart – though they have been recovering – are still holding in negative territory. This, in turn, suggests that any subsequent move-up is likely to attract fresh sellers and remain capped near the 154.00 mark. The latter coincides with the 38.2% Fibo. level, above which the USD/JPY pair could accelerate the recovery towards the 154.70-154.75 region en route to the 155.00 psychological mark.
On the flip side, the 153.00 round figure, followed by the 152.75 confluence now seems to protect the immediate downside. A convincing break below the latter would reaffirm the near-term negative outlook and drag the USD/JPY pair back below the 152.00 mark, towards the next relevant support near the 151.30-151.25 region. Spot prices could eventually drop to sub-151.00 levels, or a near two-month low touched last Friday.
Bank of Japan FAQs
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) is the Japanese central bank, which sets monetary policy in the country. Its mandate is to issue banknotes and carry out currency and monetary control to ensure price stability, which means an inflation target of around 2%.
The Bank of Japan embarked in an ultra-loose monetary policy in 2013 in order to stimulate the economy and fuel inflation amid a low-inflationary environment. The bank’s policy is based on Quantitative and Qualitative Easing (QQE), or printing notes to buy assets such as government or corporate bonds to provide liquidity. In 2016, the bank doubled down on its strategy and further loosened policy by first introducing negative interest rates and then directly controlling the yield of its 10-year government bonds. In March 2024, the BoJ lifted interest rates, effectively retreating from the ultra-loose monetary policy stance.
The Bank’s massive stimulus caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers. This process exacerbated in 2022 and 2023 due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks, which opted to increase interest rates sharply to fight decades-high levels of inflation. The BoJ’s policy led to a widening differential with other currencies, dragging down the value of the Yen. This trend partly reversed in 2024, when the BoJ decided to abandon its ultra-loose policy stance.
A weaker Yen and the spike in global energy prices led to an increase in Japanese inflation, which exceeded the BoJ’s 2% target. The prospect of rising salaries in the country – a key element fuelling inflation – also contributed to the move.
Tariffs FAQs
Tariffs are customs duties levied on certain merchandise imports or a category of products. Tariffs are designed to help local producers and manufacturers be more competitive in the market by providing a price advantage over similar goods that can be imported. Tariffs are widely used as tools of protectionism, along with trade barriers and import quotas.
Although tariffs and taxes both generate government revenue to fund public goods and services, they have several distinctions. Tariffs are prepaid at the port of entry, while taxes are paid at the time of purchase. Taxes are imposed on individual taxpayers and businesses, while tariffs are paid by importers.
There are two schools of thought among economists regarding the usage of tariffs. While some argue that tariffs are necessary to protect domestic industries and address trade imbalances, others see them as a harmful tool that could potentially drive prices higher over the long term and lead to a damaging trade war by encouraging tit-for-tat tariffs.
During the run-up to the presidential election in November 2024, Donald Trump made it clear that he intends to use tariffs to support the US economy and American producers. In 2024, Mexico, China and Canada accounted for 42% of total US imports. In this period, Mexico stood out as the top exporter with $466.6 billion, according to the US Census Bureau. Hence, Trump wants to focus on these three nations when imposing tariffs. He also plans to use the revenue generated through tariffs to lower personal income taxes.
