New Zealand Dollar remains calm above 0.6100 following NZ Budget 2024
- New Zealand Dollar (NZD) remains on the defensive on Thursday after the latest NZ government budget announcement.
- New Zealand forecasts inflation falling to below 3% in Q3 2024, to 2% around 2026.
- Investors will keep an eye out for key US data to cap off the trading week.
The NZD/USD pair edges lower around 0.6105 during the Asian session on Thursday. The release of the New Zealand budget outline for the 2024 fiscal year had little to no impact on the Kiwi as the pair remains influenced by the USD dynamic. New Zealand Finance Minister Nicola Willis stated that the Treasury sees inflation falling to below 3% in Q3 2024 and easing to 2% around 2026. The New Zealand treasury sees NZ GDP contracting in H1 2024, and growth in H2 2024.
Furthermore, New Zealand forecast a budget deficit of NZ$11.07 for the fiscal year ending June 30, 2024, wider than a deficit of NZ$9.32 billion estimated in December. The government expects a return to an obegal surplus in 2027/28.
New Zealand Dollar FAQs
The New Zealand Dollar (NZD), also known as the Kiwi, is a well-known traded currency among investors. Its value is broadly determined by the health of the New Zealand economy and the country’s central bank policy. Still, there are some unique particularities that also can make NZD move. The performance of the Chinese economy tends to move the Kiwi because China is New Zealand’s biggest trading partner. Bad news for the Chinese economy likely means less New Zealand exports to the country, hitting the economy and thus its currency. Another factor moving NZD is dairy prices as the dairy industry is New Zealand’s main export. High dairy prices boost export income, contributing positively to the economy and thus to the NZD.
The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) aims to achieve and maintain an inflation rate between 1% and 3% over the medium term, with a focus to keep it near the 2% mid-point. To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the RBNZ will increase interest rates to cool the economy, but the move will also make bond yields higher, increasing investors’ appeal to invest in the country and thus boosting NZD. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken NZD. The so-called rate differential, or how rates in New Zealand are or are expected to be compared to the ones set by the US Federal Reserve, can also play a key role in moving the NZD/USD pair.
Macroeconomic data releases in New Zealand are key to assess the state of the economy and can impact the New Zealand Dollar’s (NZD) valuation. A strong economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for NZD. High economic growth attracts foreign investment and may encourage the Reserve Bank of New Zealand to increase interest rates, if this economic strength comes together with elevated inflation. Conversely, if economic data is weak, NZD is likely to depreciate.
The New Zealand Dollar (NZD) tends to strengthen during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and are optimistic about growth. This tends to lead to a more favorable outlook for commodities and so-called ‘commodity currencies’ such as the Kiwi. Conversely, NZD tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.
Looking ahead, Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) Governor Orr will appear early Friday, and broader markets will pivot to face key US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth figures and US Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index inflation.
US Annualized Q1 GDP, slated for Thursday, is forecast to ease to 1.3% versus the previous print of 1.6%, and Core PCE Price Index inflation on Friday is expected to hold steady at 0.3% MoM in April. With investors desperate for signs of future rate cuts from the Federal Reserve (Fed), investors will be looking for signs of further easing in the US economy and cooling inflation figures.
According to the CME’s FedWatch Tool, rate markets are pricing in slightly-worse-than-even odds of at least a quarter-point Fed rate trim in September, down sharply from the 70% odds that were priced in a week and a half ago. With the US economy still outperforming expectations, a still-tight labor market, and inflation still running hotter for longer than expected, rate-cut-hungry investors are hoping for signs of economic underperformance to bolster chances of at least two rate cuts in 2024 from the Fed.
NZD/USD technical outlook
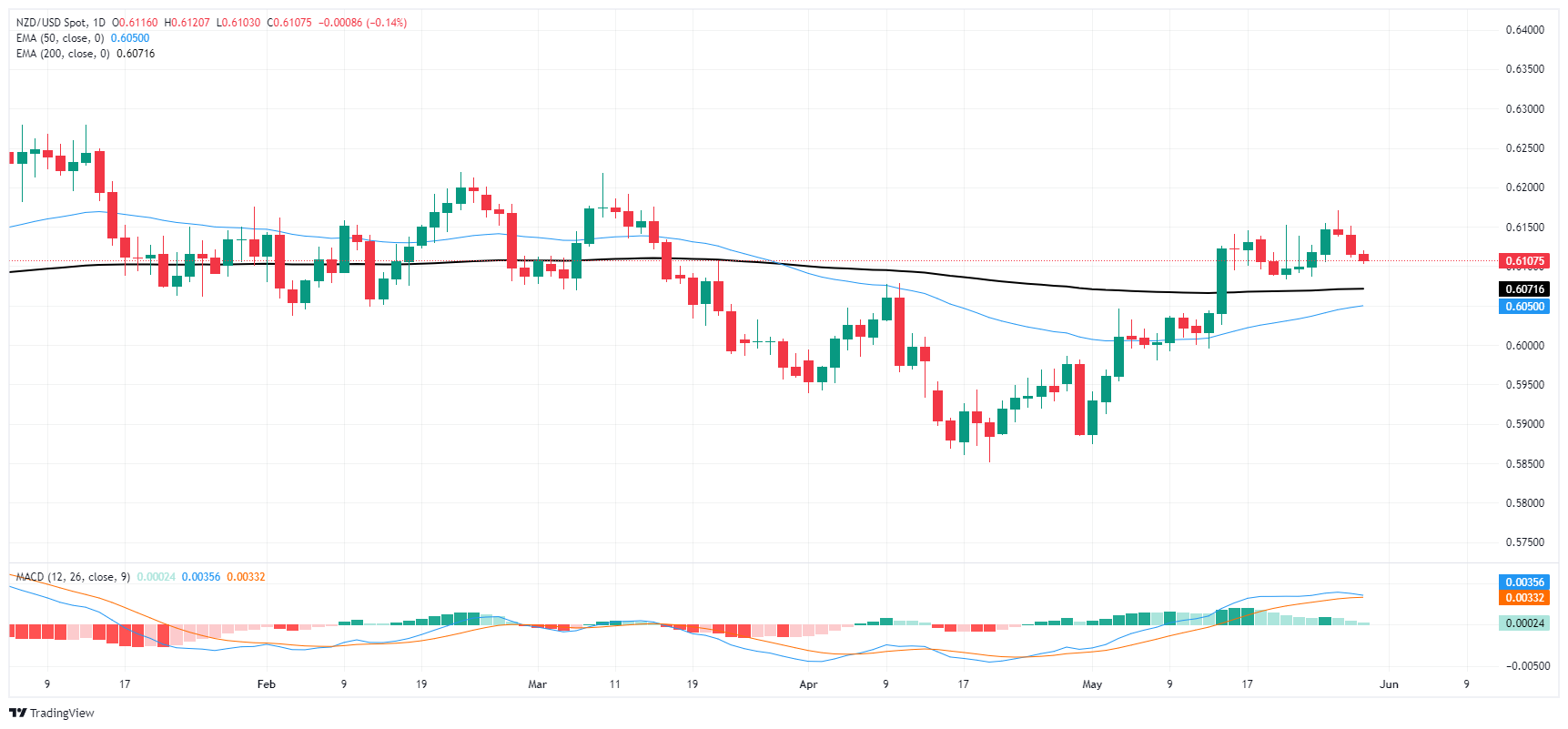
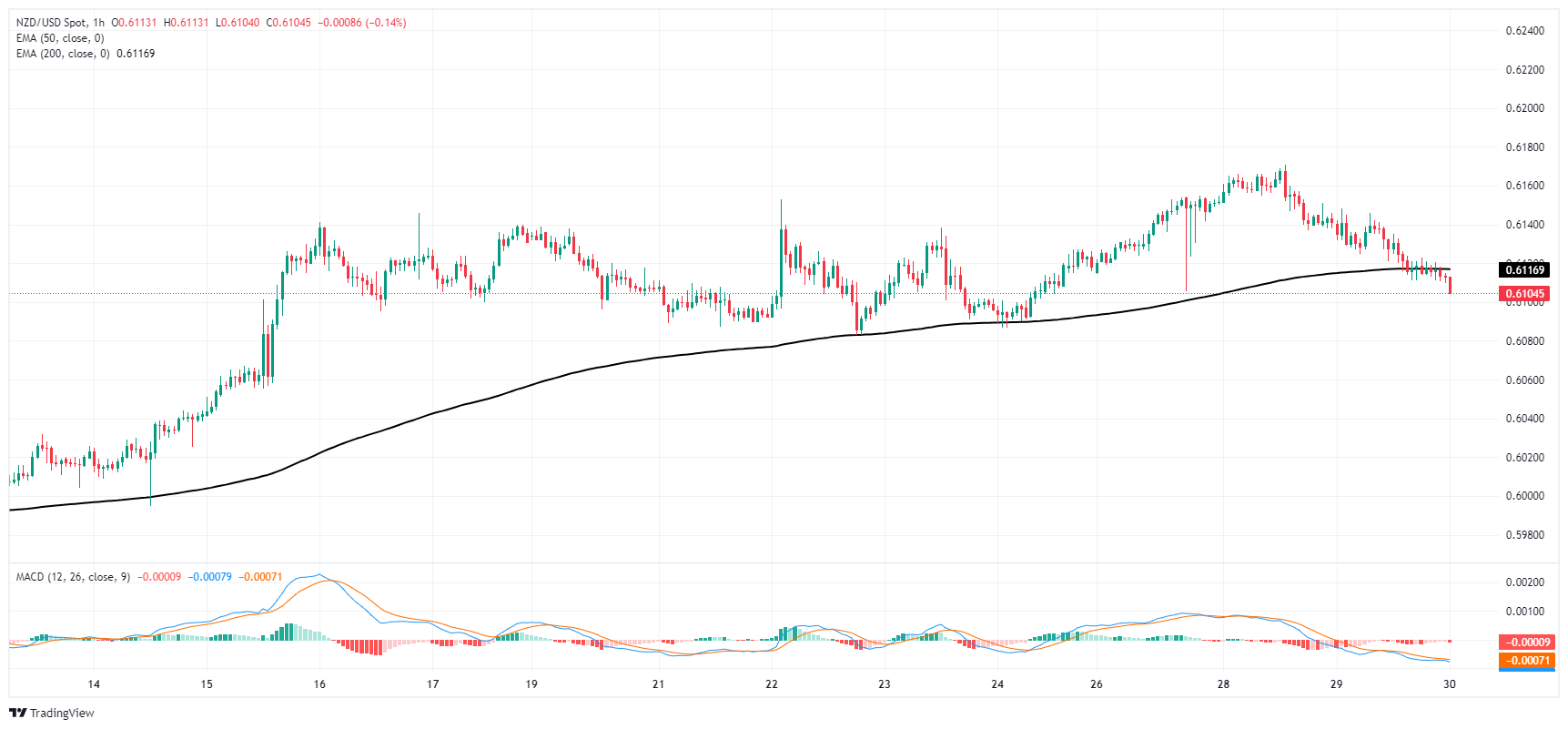
NZD/USD is trading down in the early Thursday market session, drifting towards the 0.6100 handle as broad-market Greeback strength forces down the Kiwi. The pair is heading lower for a third consecutive trading day, and bearish momentum will drag NZD/USD into the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 0.6077.
Despite near-term bearishness, the pair is still trading up from the last swing low into 0.5850 in April, and it’s buyers’ game to lose with the pair making little progress on the high side of key technical levels.